- Nain Singh Rawat
-
Pandit Nain Singh Rawat (नैन सिंह रावत) was one of the first of the pundits who explored the Himalayas for the British. He hailed from the Johaar Valley of Kumaon. He mapped the trade route through Nepal to Tibet, determined for the first time the location and altitude of Lhasa, and mapped a large section of the Tsangpo, the major Tibetan river.
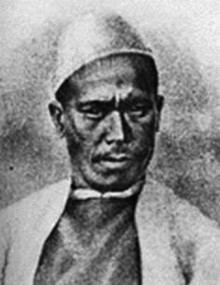 The pundit (explorer) cartographer Nain Singh Rawat (19th century CE) received a Royal Geographical Society gold medal in 1876.
The pundit (explorer) cartographer Nain Singh Rawat (19th century CE) received a Royal Geographical Society gold medal in 1876.
In 1865, with his cousin Mani Singh, Nain Singh left Dehra Dun, the Geometrical Survey of India's northern India headquarters, for Nepal. From there Mani returned to India by way of western Tibet, but Nain went on to Tashilhunpo, where he met the Panchen Lama, and Lhasa, where he met the Dalai Lama. During his stay in Lhasa, his true identity was discovered by two Kashmiri Muslim merchants residing at Lhasa, but not only did they not report him to the authorities, they lent him a small sum of money against the pledge of his watch.[1][2] Nain Singh returned to India by way of Mansarowar Lake in western Tibet.
On a second voyage, in 1867, Singh explored western Tibet and visited the legendary Thok-Jalung gold mines. He noticed that the workers only dug for gold near the surface, because they believed digging deeper was a crime against the Earth and would deprive it of its fertility.[1][3]
In 1873-75, he traveled from Leh in Kashmir to Lhasa, by a route more northerly than the one along the Tsangpo that he had taken on his first journey.[1][4]
In recognition of his prodigious feats of exploration, regarding which Colonel Henry Yule commented that "his explorations have added a larger amount of important knowledge to the map of Asia than any other living man", Nain Singh was presented with an inscribed gold chronometer by the Royal Geographic Society (RGS) in 1868. This was followed by the award of the Victoria or Patron's Medal of the RGS in 1877. The Society of Geographers of Paris also awarded Nain Singh an inscribed watch. The Government of India bestowed two villages as a land-grant to him.[5]
Contents
Legacy
On June 27, 2004, an Indian postage stamp featuring Nain Singh[6] was issued commemorating his role in the Great Trigonometrical Survey.
Recently Dr. Shekhar Pathak and Dr. Uma Bhatt, have brought out a biography of Nain Singh together with three of his diaries and the RGS articles about his travels in 3 volumes titled Asia ki Peeth Par published by PAHAR, Naini Tal - a belated but fitting tribute to the man.
See also
References
- ^ a b c Asia ki Peeth Par: Pandit Nain Singh Rawat ed. Uma Bhatt & Shekhar Pathak, Naini Tal, 2006
- ^ "Report of a Route-Survey made by PUNDIT-----,&c." by T.G.Montgomerie, The Journal of the Royal Geographic Society,Vol.38,1868
- ^ "Report of the Trans-Himalayan Explorations during 1867" by T.G.Montgomerie, The Journal of the Royal Geographic Society,Vol.39,1869
- ^ "Account of the Pundit's Journey in Great Tibet &c" by Capt. H.Trotter, The Journal of the Royal Geographic Society,Vol.47,1877
- ^ Obituary notice of Nain Singh by Col. Edmund Smyth in Proceedings of The Royal Geographical Society &c,New Monthly Series, Vol.IV, 1882: p.315-317.
- ^ Trigonometrical Survey
External links
Categories:- Indian explorers
- Explorers of Asia
- People from Uttarakhand
- Kumaon
- Explorers of the Himalayas
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
