- Caustic (optics)
-
For other uses, see Caustic (disambiguation).
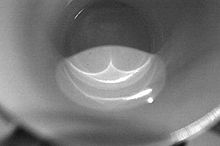
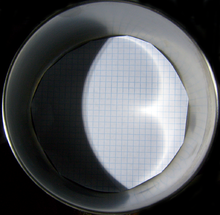
In optics, a caustic or caustic network [1] is the envelope of light rays reflected or refracted by a curved surface or object, or the projection of that envelope of rays on another surface.[citation needed] The caustic is a curve or surface to which each of the light rays is tangent, defining a boundary of an envelope of rays as a curve of concentrated light.[citation needed] Therefore in the image to the right, the caustics can be the patches of light or their bright edges. These shapes often have cusp singularities.
Such concentration of light, especially sunlight, can burn. The word caustic, in fact, comes from the Greek καυστός, burnt, via the Latin causticus, burning. A common situation where caustics are visible is when light shines on a drinking glass. The glass casts a shadow, but also produces a curved region of bright light. In ideal circumstances (including perfectly parallel rays, as if from a point source at infinity), a nephroid-shaped patch of light can be produced.[2] Rippling caustics are commonly formed when light shines through waves on a body of water.
Another familiar caustic is the rainbow.[citation needed] Scattering of light by raindrops causes different wavelengths of light to be seen in arcs of differing radius. Each such arc is a directional caustic.[citation needed]
In computer graphics, most modern rendering systems support caustics. Some of them even support volumetric caustics. This is accomplished by raytracing the possible paths of the light beam through the glass, accounting for the refraction and reflection. Photon mapping is one implementation of this. Some examples of 3D ray-traced caustics can be found here.
See also
References
- ^ Lynch DK and Livingston W (2001). Color and Light in Nature. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521775045. Chapter 3.16 The caustic network, Google books preview
- ^ Circle Catacaustic. Wolfram MathWorld. Retrieved 2009-07-17.
- Born, Max; and Wolf, Emil (1999). Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light (7th ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-64222-1.
- Nye, John (1999). Natural Focusing and Fine Structure of Light: Caustics and Wave Dislocations. CRC Press. ISBN 9780750306102.
Further reading
- Ferraro, Pietro (1996). "What a caustic!". The Physics Teacher 34 (9): 572. Bibcode 1996PhTea..34..572F. doi:10.1119/1.2344572.
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.