- Nuclear reactor core
-
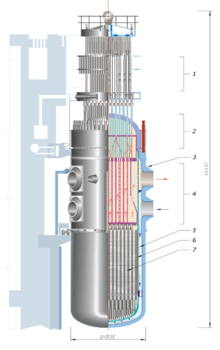 Example of the core of a nuclear power plant, a VVER design.
Example of the core of a nuclear power plant, a VVER design.
A nuclear reactor core is the portion of a nuclear reactor containing the nuclear fuel components where the nuclear reactions take place.
Contents
Description
The nuclear reactor core (also referred to as the "reactor core" or the "core") is the region within a nuclear reactor where the nuclear fuel assemblies are located and the nuclear reaction consequently takes place. The core of the reactor contains all the nuclear fuels and generates all of the heat. It contains low-enriched uranium, control systems and structural materials. The core contains hundreds of thousands of individual fuel pins.
Water-moderated reactors
Inside the core of a typical pressurized water reactor or boiling water reactor are nuclear fuel rods equivalent to the diameter of a large gel type ink-pen, each about 12 feet (3.7 m) long, which are grouped by the hundreds in bundles called "fuel assemblies". Inside each fuel rod, pellets of uranium, or more commonly uranium oxide, are stacked end to end. Also inside the core are control rods, filled with pellets of substances like boron or hafnium or cadmium that readily capture neutrons. When the control rods are lowered into the core, they absorb neutrons, which thus cannot take part in the chain reaction. Conversely, when the control rods are lifted out of the way, more neutrons strike the fissile uranium-235 (U-235) or plutonium-239 (Pu-239) nuclei in nearby fuel rods, and the chain reaction intensifies.
The heat of the fission reaction is removed by the water, which also acts to moderate the neutron reactions.
An alternative form of nuclear fuel would be fissile uranium-233 (U-233) made by the neutron-bombardment of the common thorium-232.
Graphite-moderated reactors
Graphite Molten-Salt Reactor Experiment core
There are also Graphite moderated reactors in use.
One type uses solid graphite for the neutron moderator and ordinary water for the coolant. See the Soviet-made RBMK nuclear-power reactor. This was the type of reactor involved in the Chernobyl disaster.
In the advanced gas-cooled reactor, a British design, the core is made of a graphite neutron moderator where the fuel assemblies are located. Carbon dioxide gas acts as a coolant and it circulates through the graphite removing heat.
There have also been several experimental reactors that use graphite for moderation, such as the pebble bed reactor concepts and the molten-salt reactor experiment (graphite core shown at right).
See also
- China Syndrome or severe Nuclear meltdown
- Lists of nuclear disasters and radioactive incidents
- Nuclear power
- Nuclear reactor technology
References
- Nuclear Reactor Analysis, John Wiley & Sons Canada, Ltd.
Categories:- Nuclear power plant components
- Nuclear technology
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

