- Diisopropyl tartrate
-
Diisopropyl tartrate 
 Diisopropyl tartrateOther namesBis(1-methylethyl) ester of 2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic acid, Dipropan-2-yl 2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate, DIPT
Diisopropyl tartrateOther namesBis(1-methylethyl) ester of 2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic acid, Dipropan-2-yl 2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate, DIPTIdentifiers CAS number 2217-15-4 
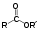
PubChem 102768 EC number 218-709-0 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC(C)OC(=O)C(C(C(=O)OC(C)C)O)O
Properties Molecular formula C10H18O6 Molar mass 234.25 g/mol Boiling point 152 °C (425.2 K) at 16 kPa
 tartrate (verify) (what is:
tartrate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Diisopropyl tartrate (DIPT) is a diester of tartaric acid. It has a two chiral carbon atoms giving rise to three stereoisomeric variants. It is commonly used in asymmetric synthesis as a catalyst and as chiral building block for pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. Its main application is in Sharpless epoxidation, where it serves as a chiral ligand to titanium after reaction with titanium isopropoxide.[1]
References
- ^ Katsuki, Tsutomu; Sharpless, K. Barry (1980). "The first practical method for asymmetric epoxidation". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 102 (18): 5974. doi:10.1021/ja00538a077.
This article about an ester is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
