- para-Azoxyanisole
-
para-Azoxyanisole 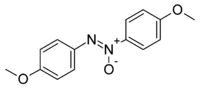 1-methoxy-4-[(4-methoxyphenyl)-NNO-azoxy]benzeneOther namesp-Azoxyanisole
1-methoxy-4-[(4-methoxyphenyl)-NNO-azoxy]benzeneOther namesp-AzoxyanisoleIdentifiers CAS number 1562-94-3 PubChem 15277 ChemSpider 14542 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - COc2ccc(\N=[N+](/[O-])c1ccc(OC)cc1)cc2
Properties Molecular formula C14H14N2O3 Molar mass 258.27 g/mol Density 1.14g/cm3 Melting point 114.9 °C, 388 K, 239 °F
Boiling point 417.9°C @ 760mmHg
Hazards Flash point 206.6°C  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references para-Azoxyanisole (PAA) is an organic, aromatic compound. In a solid state, it appears as a white powder, but when heated it forms a liquid crystal. As one of the first known and most readily prepared liquid crystals,[1] PAA has been played an important role in the development of liquid crystal displays.[2]
Its liquid crystal range is from 118 °C to 136 °C. The solid to nematic transition is at 118 °C and the nematic to isotropic liquid transition at 136 °C.[1]
References
- ^ a b Shao, Y.; Zerda, T. W. (1998). "Phase Transitions of Liquid Crystal PAA in Confined Geometries". Journal of Physical Chemistry B 102 (18): 3387–3394. doi:10.1021/jp9734437.
- ^ Liquid Gold: The Story of Liquid Crystal Displays and the Creation of an Industry, Joseph A. Castellano, ISBN 978-9812389565
Categories:- Azo compounds
- Amine oxides
- Liquid crystals
- Phenol ethers
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
