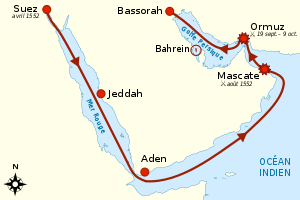
- Ottoman campaign against Hormuz
-
Ottoman campaign against Hormuz
(1552-1554)Part of Ottoman–Portuguese Conflicts (1538–1557)
Piri Reis expedition against Ormuz, and Ottoman Indian Ocean fleet.Date 1552-1554 Location Persian Gulf Result indecisive Belligerents  Portuguese Empire
Portuguese Empire Ottoman Empire
Ottoman EmpireCommanders and leaders Piri Reis Strength unknown 4 galleons
25 galleys
850 troopsCasualties and losses unknown unknown Portuguese battles in the Indian OceanCannanore (1501) –Calicut (1502) – Cochin (1504) – Cannanore (1506) – Anjadiva (1506) – Ormuz (1507) – Cannanore (1507) – Chaul (1508) – Dabul (1508) – Diu (1509) – Goa (1510) – Malacca (1511) – Calicut (1526) – Chalium (1531) – Diu (1538) –Diu (1546) – Aden (1548) – Hormuz campaign – (Muscat – Gulf of Oman) – Malacca (1568) – Malacca (1606) –Battle of Cape Rachado (1606) – Swally (1612) – Ormuz (1622) – Action of one February (1625) – River Duyon (1629) – Goa (1638) – Calicut (1752)The Ottoman campaign against Hormuz took place in 1552-54. An Ottoman fleet led by Admiral Piri Reis and Seydi Ali Reis was dispatched from the Ottoman harbour of Suez to eliminate the Portuguese presence from the northwestern part of the Indian Ocean, and especially their fortress at Hormuz Island.
Contents
Preliminaries
The Ottomans were able to take possession of Basra from Persia during the Ottoman–Safavid War (1532–1555). The Ottomans were then able to capture several key positions in the Persian Gulf. In 1550, they captured Qatīf.[1]
In the 1552-54 expedition, the Ottoman force consisted in 4 galleons, 25 galleys, and 850 troops, dispatched from the Ottoman harbour of Suez.[2]
Sieges of Muscat and Hormuz
The fleet managed to chase the Portuguese from Muscat, modern Oman, in August 1552 in the Capture of Muscat. Soon however the Ottomans departed. However, they were unsuccessful in the Siege of Hormuz in September 1552.[1]
Ultimately, the fleet managed to occupy and control the coasts of Yemen, Aden and Arabia, as far north as Basra, so as to facilitate their trade with India.[2] The fleet went up to Basra, then an Ottoman harbour. They were able to capture Bahrain in 1554.[1]
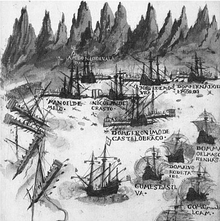 Seydi Ali Reis and his galleys taken in an ambush by Portuguese forces while trying to bring back his float from Basra to Suez in August 1554.
Seydi Ali Reis and his galleys taken in an ambush by Portuguese forces while trying to bring back his float from Basra to Suez in August 1554.
Meanwhile, during the year 1553, Seydi Ali Reis was leading an expedition against the Portuguese into the India Ocean, but he was unsuccessful.[1]
Seydi Ali Reis and his galleys would be taken in an ambush by Portuguese forces while he was trying to bring back his float from Basra to Suez in August 1554.
See also
- Capture of Aden (1548)
Notes
 Major Ottoman siegesPrusa (1326) • Nicaea (1331) • Nicomedia (1333) • Sofia (1385) • Tarnovo (1393) • Constantinople (1422) • Thessalonica (1422) • Svetigrad (1448) • Constantinople (1453) • Belgrade (1456) • Kruje (1478) • Rhodes (1480) • Otranto (1481) • Cairo (1517) • Rhodes (1522) • Algiers (1529) • Vienna (1529) • Güns (1532) • Tunis (1534) • Baghdat (1534) • Klis (1537) • Corfu (1537) • Diu (1538) • Aden (1538) • Castelnuovo (1539) • Buda (1541) • Nice (1543) • Esztergom (1543) • Van (1547) • Tripoli (1551) • Muscat (1552) • Hormuz (1552) • Eger (1552) • Oran (1556) • Oran (1563) • Malta (1565) • Szigetvar (1566) • Tunis (1574) • Gvozdansko (1578) • Sisak (1593) • Baghdad (1638) • Candia (1669) • Kamenets (1672) • Vienna (1683) • Belgrade (1739)Categories:
Major Ottoman siegesPrusa (1326) • Nicaea (1331) • Nicomedia (1333) • Sofia (1385) • Tarnovo (1393) • Constantinople (1422) • Thessalonica (1422) • Svetigrad (1448) • Constantinople (1453) • Belgrade (1456) • Kruje (1478) • Rhodes (1480) • Otranto (1481) • Cairo (1517) • Rhodes (1522) • Algiers (1529) • Vienna (1529) • Güns (1532) • Tunis (1534) • Baghdat (1534) • Klis (1537) • Corfu (1537) • Diu (1538) • Aden (1538) • Castelnuovo (1539) • Buda (1541) • Nice (1543) • Esztergom (1543) • Van (1547) • Tripoli (1551) • Muscat (1552) • Hormuz (1552) • Eger (1552) • Oran (1556) • Oran (1563) • Malta (1565) • Szigetvar (1566) • Tunis (1574) • Gvozdansko (1578) • Sisak (1593) • Baghdad (1638) • Candia (1669) • Kamenets (1672) • Vienna (1683) • Belgrade (1739)Categories:- Suleiman the Magnificent
- Piri Reis
- Conflicts in 1552
- Military campaigns involving the Ottoman Empire
- Sieges involving Portugal
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.