- Nymphaion (Crimea)
-
For other uses of this term, see Nymphaion (disambiguation).
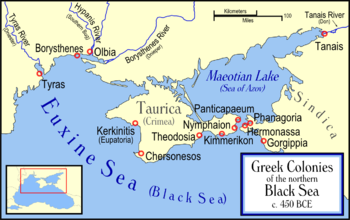
Nýmphaion (Greek: Νύμφαιον, Latin: Nymphaeum, Russian: Нимфей) was a significant centre of the Bosporan Kingdom, situated on the Crimean shore of the Cimmerian Bosporus, about 17 kilometers south of Panticapaeum.
There was a Scythian settlement before the Greek colonists set up an emporium on the site in the 6th century BC. The town issued its own coins and generally prospered in the period of Classical antiquity, when its citizens controlled cereal trade, which was vital for the well-being of mainland Greece. Athens chose it as its principal military base in the region ca. 444 BC and Gylon, the grandfather of Demosthenes, suffered banishment from Athens on charges that he had betrayed Nymphaeum during the Peloponnesian War. It was annexed to the Bosporan Kingdom by the end of the century.
During the Mithridatic Wars, the town allied with the Roman Republic and withstood a siege by the army of Pharnaces II of Pontus. It was at Phanagoria that the insurrection broke out against Mithridates VI of Pontus, shortly before his death; and his sons, who held the citadel, were obliged to surrender to the insurgents. An inscription found during excavations testifies that Queen Dynamis honored Augustus as "the emperor, Caesar, son of god, the god Augustus, the overseer of every land and sea". The loyalty to Rome allowed Phanagoria to maintain a dominant position in the region until the 4th century, when it was sacked and destroyed by the invading Huns.
The site occupied a small hill by the sea. The acropolis contained the temples of Aphrodite (with several rooms) and of the Cabeiri. The lower terrace by the sea centred on the sanctuary of Demeter, first erected in the 6th century BC and several times rebuilt. Other ruins indicate that the town's architecture was unusually refined, perhaps the most sophisticated in the Bosporan Kingdom. One structure has no parallels in the Hellenistic world: it goes back to the 3rd century BC and is built of rose marl. The site also yielded a number of terracotta figurines, winemaking facilities (the oldest along the northern shore of the Black Sea) and several horse burials, associated with the Sarmatians.
References
- The Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites. (eds. Stillwell, Richard. MacDonald, William L. McAlister, Marian Holland). Princeton University Press, 1976. ISBN 0-691-03542-3.
North Pontic Greek colonies Tyras · Olbia · Borysthenes · Eupatoria · Chersonesos · Charax · Theodosia · Kimmerikon · Nymphaion · Tyritake · Panticapaeum · Myrmekion · Kepoi · Phanagoria · Hermonassa · Gorgippia · Pityus · Dioscurias · Tanais
 Categories:
Categories:- Ancient Greek cities
- Pontic Greeks
- Greek colonies in Crimea
- Former populated places in Eastern Europe
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.