- North Lombok Regency
-
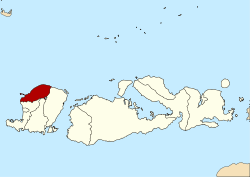
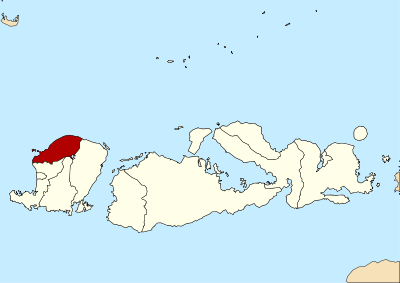
North Lombok Regency
Kabupaten Lombok Utara— Regency — 
SealMotto: Tioq Tata Tunaq Location of North Lombok Regency in West Nusa Tenggara Location in Indonesia Coordinates: 8°21′S 116°9′E / 8.35°S 116.15°ECoordinates: 8°21′S 116°9′E / 8.35°S 116.15°E Country Indonesia Province West Nusa Tenggara Capital Tanjung Government – Type Kabupaten-Regency – Bupati Area – Land 776.25 km2 (299.7 sq mi) Elevation
at Mount Rinjani summitmax 3,726 m (12,224 ft) Population – Total 210,848 Demographics – Ethnic groups Sasak, Balinese, Javanese, Sumbawa people, Flores people – Religion Muslim, Hindu, Christian, Buddhist – Languages Indonesian (official), Sasak Time zone WITA (UTC+8) Website http://www.lombokutarakab.go.id/ North Lombok Regency (Indonesian: Kabupaten Lombok Utara) is a Kabupaten of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Lombok and the capital is Tanjung situated on the north west coast of the island.
The symbolism behind the Lambang of Kabupaten Lombok Utara, (the regions symbolic logo) is to describe the society of North Lombok as a faithful and obedient people unified under the Republic of Indonesia in a community having a tradition of integrity, religious strength and awareness of the cosmos. These principles providing a strong base for the people of North Lombok to work together in a disciplined and responsible society building a prosperous and ordered community.[1] The motto of the region is "Tioq Tata Tunaq"[1]
Contents
Location
North Lombok Regency is bounded by the Java Sea to the north, Central Lombok Regency and West Lombok to the south, East Lombok Regency to the east and the Lombok Strait to the west. Central to the region is Mount Rinjani which at 3,726 metres (12,224 ft) is the third highest mountain the second largest volcano in the country and is and an active volcano.[2] The oldest recorded historical eruption was in 1847 and last eruption was in May 2010[3][4][5][6][7][8]
History
The Regency of West Lombok was established in 1958 and included the northern section of Lombok now established as the Regency of North Lombok. The West Lombok Administrative Region previously oversaw the West coast, Ampenan, Tanjung, Bayan, Gerung, Gondang and Cakranegara.
In 1993 the West Lombok district was separated into two autonomous regions. As a consequence of the formation of the Government of Mataram in year 2000 the capital of West Lombok was moved from Mataram, West Lombok to Gerung in the south of the district. This move resulted the 5 districts in the northern end of the island being too far away from the services of the West Lombok District at Gerung. Subsequently and with the full support of the local government of West Lombok regency North Lombok established its own regional government situated at Tanjung and the north of the island now functions autonomously from the West Lombok Regency.[9][10] The Regency was ratified Law Number 26 Year 2008, creating the Regency from within the existing boundaries of is a division of the West Lombok Regency .
Central to the region is Mount Rinjani which at 3,726 m is the third highest mountain the second largest volcano in the country and is and an active volcano The oldest recorded historical eruption was in 1847 and last eruption was in may 2010. Gunung Rinjani Observation Post Rinjani Sembalun is located in the village of Lawang, Sub Sembalun 12.5 km (4000 feet) northeast of G. Rinjani). Observers at this post monitor G.Rinjani, and G.Barujari[4][11]
Rinjani eruptive history
Rinjani erupted three times on May 22, 2010 with activity continuing until early on May 23. According to the volcano's official monitoring agency, ash from Mount Barujari was reported as rising up to two km into the atmosphere and damaged crops. The volcano did not threaten villagers at that time. Lava flowed into the caldera lake, pushing its temperature up from 21°C to 35°C, while smoke spread 12 km.[12] In February 2010 observers at the Gunung Rinjani Observation Post located 12.5 km (4000 feet) NE of Rinjani saw one whitish-colored plume that rose 100 metres (328 ft) from the volcano. Dense whitish plumes (and possibly brown) rose 500 metres (1,640 ft) - 900 metres (2,953 ft) in March 2010 on 26 occasions and as high as 1,500 metres (4,921 ft) in April 2010 on 41 occasions. Plumes seen on 1 and 2 May 2010 were "chocolate" in color and rose a maximum height of 1,600 metres (5,249 ft). From February 2010 through April 2010 seismicity decreased, although the maximum amplitude of earthquakes increased. CVGHM (Center of Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation)[13] also noted that ash eruptions and ejected incandescent material fell within Rinjani caldera, but some ash was blown out of the caldera.[14] Please see main Rinjani article for more detail.
Administration
Administrative structure
Kabupaten Lombok Barat (West Lombok Regency) is one of Lombok's four Regencies or administrative regions.
- TGH M Zainul Majdi, MA., Governor of NTB (West Nusa Tenggara), (Mataram is the Provincial Capital of West Nusa Tenggara).
- H. Djohan Sjamsu, SH. Regent (Bupati) of Kabupaten Lombok Utara (North Lombok Regency). Inaugurated on 2 August 2010, Tanjung, North Lombok.
- SH dan H. Najmul Akhyar, SH, MH. Vice Regent (Wakil Bupati) inaugurated 2 August 2010, Tanjung, North Lombok.
Administrative boundaries
Boundary District Regency North Java Sea South Batu Layar
PrayaWest Lombok Regency
Central Lombok RegencyWest Lombok Strait East Praya East Lombok Regency In late September 2010, a border dispute emerged over the new regional boundaries. Central to the dispute was the new border dividing the North Lombok Regency from West Lombok Regency at a point where it traversed the village of Lembah Sari situated west of Pemenang. Villagers from the 14 hamlets that form Lembah Sari felled a large tree on the side of the main inland road connecting the northern region to that of West Lombok Regency and the City of Mataram so that it formed a roadblock and then manned the roadblock in protest to the boundary alignment. Residents to the decision to move an apparent border between the two districts that followed the line of division between West Pemenang and Lembah Sari. A police detachment later re-opened the road to allow workers from West Lombok Regency to commence work to clear the road. Limited thru traffic was restored after 7 hours of blockade. The North Lombok Regency made public statements to clarify that district authorities would abide by whatever decision was made by the provincial government regarding regional boundaries. 34 villages that were formerly part of West Lombok are now part of North Lombok.[15]
District organisation
North Lombok Regency consists of five Kecamatan or districts. It is bounded by the Java Sea to the north, the West Lombok Regency to the south, Central Lombok Regency to the south and East Lombok Regency on the east side and the Lombok Strait to the west
Kecamatan
- Bayan
- Gangga,
- Kayangan
- Tanjung
- Pemenang
Population
The majority of the population are Sasak people. In 2008 East Lombok Regency recorded a total of 1.068.486 persons resident being 494.149 males and 574.337 females.[16]
In 2010 East Lombok Regency recorded 1,081,630 persons in the decennial census, 24.7% being officially below Indonesian poverty level[17] This regency is primarily Muslim, with few people of Balinese origin compared with West Lombok.
Ethnicity
The Sasak people are the indiginous people of Lombok and form the majority of north Lombok's residents. north Lombok is also home to people of Balinese, Chinese, Tionghoa-peranakan people of mixed Indonesian and Chinese descent and small number of Arab Indonesian people, mainly of Yemeni descent who originally settled in the early port city of Ampenan.
Religion
Islam is the religion of the majority population of north Lombok. Other religion's practised in east Lombok are Christianity, Catholicism, Hinduism, Buddhism, and Confucianism.
The northern part of Lombok is home to the Wektu Telu ("Three times"), who as the name suggests pray only three times daily, instead of the five times stipulated in the Quran. Many of the Waktu Telu beliefs are entwined with animism. Waktu Telu has influences not only of Islam, but also Hinduism and pantheistic beliefs. There are also remnants of Boda (people without a religion) who maintain Pagan Sasak beliefs. There is some considerable uncertainty about this though as others believe that the term Buda was simply a pejorative term used by the Islamized Sasak to indicate those groups that refused to convert to Islam. If this hypothesis is true, the remnants of the Boda religion can be seen as representing a kind of original Sasak culture, undiluted by later Islamic innovations.[18] Many influences of animist belief still prevail within the Sasak people and most Sasak people believe strongly in the existence of spirits or ghosts. These original Sask belief systems appear to be much stronger in the Northern areas of Lombok than elsewhere on the island The sasak people regard both food and prayer as indispensable whenever they seek to communicate with spirits, including the dead [19] and many ritualistic traditional Sasak practices still endure despite the influences of both modernity and orthodox Islam. This is discussed in more detail in the Lombok article.
Language
Most people in north Lombok normally the Sasak language. Bahasa Sasak is the native language of the indigenous people of Lombok. Bahasa Indonesian is the language most widely used in everyday interactions at places such as the larger hotels and in the government offices. When at home or a place of recreation north Lombok residents tend to use local northern Lombok dialects of the Sasak language.
Land use
Plantation sector
In August 2010 the Deputy Governor of West Nusa Teggara (NTB), Ir H Badrul Munir, MM, announced in Tanjung, North Lombok Regency, that the District of North Lombok has the potential to be developed as a plantation area, and as a national center for cocoa development in NTB, this region is rich with agricultural commodities such as cocoa, coffee, vanilla, and cloves.[20][21]
Education
Transportation
Small public ferries provide passenger access between Bangsal harbour and the Gili Islands. These are operated by the Sea Transportation Maritime Co-operative (Koperasi Angkutan Laut Karya Bahari). The Koperasi is in principal a community co-operative and they operate three boat services; the Public Boat, the Shuttle boat, the Island Hopping boat and also offer (official) Charter boats. The craft are principally of local design and wooden construction powered by petrol fuelled outboard engines. Prices are set by Kebupaten decree, the pricing of current operations is defined by Pengumuman Dinas Perhubungan Lombok Barat no.:551/662/V/dishub tanggal 26 Mei 2008. Informal private charter services also serve the Bangsal-Gili islands routes and inter-island traffic.
Small high speed passenger craft such as speedboats connect the Gili Islands to Teluk Nare on the Lombok mainland immediately to the east of the Gili islands and Senggigi a little further south along the coast. Speedboat services are also available for local in-shore charters from Teluk Nare a little south of Bangsal and at Gili islands. The majority of the speedboat services are owned and operated by the local hotels and dive shops.
Fast boat services are small high speed craft operating multiple daily scheduled high speed boat services across the Lombok Strait westward to Bali. The craft are of light duty construction having either fibreglass or aluminium hulls and are powered by petrol fuelled outboards. Significant operational and safety issues plague these vessels and the operators.
In August 2010 the Deputy Governor of West Nusa Teggara (NTB), Ir H Badrul Munir, MM, announced plans for the government to assist development in the tourism sector in North Lombok. These plans, including improvements to land and sea transportation infrastructure are intended to assist with the tourist traffic going to the three Gili islands. Improvements are to include safety, convenience and transit time for operations of the public ferry co-operative providing the services crossing between Bangsal and Gili Trawangan[20]
Passenger and vehicle ferries:
- Lombok Strait: Tanjung Lembar Lombok - Padang Bai, Bali, with 12 ferries providing crossings once every hour.
- Alat Strait: Labuhan Lombok - Pototano, Sumbawa with 8 ferries providing 18 crossings per day.[22]
These drive on, drive off ferries provide the principal facilities for road transport movements in and out of Lombok. Disruptions on these routes can significantly effect trade and the provision of supplies to the island as the shipping operators on these routes will often suspend services due to breakdown or heavy seas.
Tanjung Lembar seaport in the southwest of the island provides facilities for small freighters and fishing boats.
Public buses and Bemo run both along the west coast from the south and through Pusuk pass to connect to Mataram and Cakranegara. Limited services are available on the east coast to connect to Praya and south toward Kuta.
North Lombok is served by the Lombok International Airport (Bandara Internasional Lombok) (IATA: ---, ICAO: WADL).
Lombok International Airport in Central Lombok commenced operations on 1 October 2011 replacing the previous international and domestic facilities at Selaparang Airport near Ampenan in West Lombok Regency which formally closed for operations on the evening of 30 September 2011. All services previously operated at the Selaparang airport were moved across to the new airport at that time.
Limited Helicopter charter is available from Bali and light fixed wing charter is available from both Lombok and Bali.
Tourism
The northern region of Lombok holds two of the islands most significant tourism attractions, Mount Rinjani and the Gili Islands.
On the west coast this touristic region starts just north of the township of Senggigi at Klui beach and runs northward toward the northern townships of Pemenang and Tanjung. Bangsal and Tanjunk Teluk near Pemenang provide services connecting across the short distance of water to the Gili islands off the Sire Penninsular just south of Tanjung. A little further to the north are Bayan and Senaru which offer the main gateways to access Mount Rinjani.Gunung Rinjani National Park (Taman Nasional Gunung Rinjani) is popular for mountain climbs and trekking and represents an important nature reserve and water catchement area. The park is officially 41,330 hectares within the park boundaries and a further 66,000 hectares of protected forest outside. The mountain and its satellites form the Mount Rinjani National Park (Taman Nasional Gunung Rinjani) - officially 41,000 hectares within the park boundaries and includes a further 66,000 hectares of protected forest outside. In 2008, the Indonesian government proposed to UNESCO that Mount Rinjani be one of the world's official geoparks. If this was approved by UNESCO, Mount Rinjani would become the first such geological park in Indonesia.[23][24][25][26]
- See the article on Mount Rinjani for more information.
Kosaido Golf Club is an international 18 holes championship course located on the Sire Peninsula in Tanjung. The course has views of Mt. Rinjani to the north east and the Gili Islands across the bay to the west. The course was designed by Peter Thompson, Michael Wolveridge & Perrett and pays respect to the natural onsite contours of the land. The 18 holes championship course offers a basic clubhouse facility and is promoted as having a unique, challenging and world class experience for golfers of all levels.[27]
Marina facilities
The newly established Medana Bay Marina at Medana Bay near Tanjung has twenty five mooring buoys in more than 5m of water for 35 ft to 45 ft vessels and anchorage space for another twenty vessels.[28] The marina facilities were established in 2009 and hosted over 90 yacht during the Sail Indonesia event in September 2009.
Medana Bay Marina
- Medana Bay Marina is at: 8° 21.83'S 116° 07.75'E, (Traditional system: 8°21'50'S 116°07'45'E") and is situated at Medana Bay, Tanjung, North Lombok.
- The mooring basin is centred on 08°21.833’S and 116°07.750’E with an approach transit point almost due north at 08°20.432’S and 116°07.685’E.
- A current Sea Chart and sea approach tracks are available on the Marina's website [2]. Medana Bay is sometimes called Teluk Dalam, meaning Deep Bay.
In late July 2010 participants of Sail Indonesia – Sail Banda 2010 set sail from Darwin Sailing Club in northern Australia. After congregating in Labuhan Bajo on the western tip of Flores in early September 2010 they moved on to Medana Bay on the north-western coast of Lombok prior to moving on to Bali and Kalimantan. Medana Bay was an official stop-over on the itinerary.[29] A repeat of the event is anticipated in 2011, departing Darwin on 23 July 2011, however a stop in Lombok is not on the itinerary.[30]
References
- ^ http://www.lombokutarakab.go.id Kabupaten Lombok Utara the Regency of North Lombok
- ^ "Information - Rinjani". Global Vulcanism Program USGS-Smithsosian. http://www.volcano.si.edu/world/volcano.cfm?vnum=0604-03=. Retrieved 13 Sept 2010.
- ^ "Mountains of the Indonesian Archipelago-92 Mountain Summits with Prominence of 1,500 meters or greater". Jonathan de Ferranti and Aaron Maizlish. first listing, August 16, 2005. http://www.peaklist.org/WWlists/ultras/indonesia.html. Retrieved 13 Sept 2010.
- ^ a b "Global Vulcanism Program-Rinjani Eruptive History". Global Vulcanism Program. May 2-Dec20 2009. http://www.volcano.si.edu/world/volcano.cfm?vnum=0604-03=&volpage=erupt. Retrieved 2010-05-10.
- ^ "Global Volcanism Program | Rinjani | SI / USGS Weekly Volcanic Activity Reports". Volcano.si.edu. http://www.volcano.si.edu/world/volcano.cfm?vnum=0604-03=&volpage=weekly#Apr2010. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- ^ "Pusat Vulkanologi & Mitigasi Bencana Geologi - VSI - Evaluasi Kegiatan G. Rinjani". Portal.vsi.esdm.go.id. 2010-05-04. http://portal.vsi.esdm.go.id/joomla/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=594&Itemid=1. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- ^ "SI / USGS Weekly Volcanic Activity Report-5–11 May 2010-RINJANI Lombok Island (Indonesia)". Global Volcanism Program=5–11 May 2010. http://www.volcano.si.edu/reports/usgs/. Retrieved 2010-05-17.
- ^ "Volcano erupts in Indonesia". Australian Broadcasting Commission-ABC Asia Pacific News Service 24 may2010. http://www.radioaustralianews.net.au/stories/201005/2907089.htm?desktop. Retrieved 2010-05-24.
- ^ http://www.lombokutarakab.go.id/ Kabupaten Lombok Utara the Regency of North Lombok|downloaded 29 Aug 2010
- ^ http://www.lombokbaratkab.go.id/ Kabupaten Lombok Barat, the Regency of West Lombok|downloaded 29 Aug 2010
- ^ "Pusat Vulkanologi & Mitigasi Bencana Geologi - VSI - Contact". Portal.vsi.esdm.go.id. http://portal.vsi.esdm.go.id/joomla/index.php?option=com_contact&task=view&contact_id=1&Itemid=59. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- ^ "Volcano erupts in Indonesia". Australian Broadcasting Commission-AsiaPacific News Center. http://www.radioaustralianews.net.au/stories/201005/2907089.htm?desktop. Retrieved 2010-05-24.
- ^ "Pusat Vulkanologi & Mitigasi Bencana Geologi - VSI - Home". Portal.vsi.esdm.go.id. http://portal.vsi.esdm.go.id/joomla/. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- ^ "SI / USGS Weekly Volcanic Activity Report-RINJANI Lombok Island (Indonesia) 8.42°S, 116.47°E; summit elev. 3726 m". Global Vulcanism Program Program. 28 April-4 May 2010. http://www.volcano.si.edu/reports/usgs/index.cfm?wvarweek=20100428#rinjani. Retrieved 2010-05-09.
- ^ "In Lombok, a Moved Border Causes Temperatures to Rise". Jakarta Globe (online). 27 Sept 2010. http://www.thejakartaglobe.com/news/in-lombok-a-moved-border-causes-temperatures-to-rise/398401. Retrieved 28 Sept 2010.
- ^ "Jumlah Penduduk dan Rasio Jenis Kelamin Menurut Kabupaten/Kota di Provinsi NTB Tahun 2008". Badan Pusat Statistik Provinsi Nusa Tenggara Barat. 11 December 2009. http://ntb.bps.go.id/index.php/kependudukan/51-jumlah-penduduk-dan-rasio-jenis-kelamin-tahun-2008. Retrieved 31 August 2010.
- ^ "Liputan6 :: Lombok Timur Pemasok Utama TKI NTB". Berita.liputan6.com. 2010-08-28. http://berita.liputan6.com/bnp2tki/201008/293575/Lombok.Timur.Pemasok.Utama.TKI.NTB. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- ^ Temenos 32 (1996), 7-36. Sven Cederroth, From Ancestor Worship to Monotheism, Politics of Religion in Lombok
- ^ K. Telle, Feeding the dead; Reformulating Sasak mortuary practices: Bijdragen tot de Taal, Land-en Volkenkunde 156 (2000), no: 4, Leiden, 771-805
- ^ a b "KLU Cocoa Development Center will be made in NTB". NTB Provincial Government. 13 Aug 2010. http://ntbprov.go.id/baca.php?berita=19. Retrieved 2 Sept 2010.
- ^ "Kabupaten Lombok Utara has potential to be a chocolate-producing areas nationwide (KLU berpotensi jadi daerah penghasil coklat berskala nasional)". SuaraKomunitas 2010/ Belle FM. 2 October 2010. http://ntbprov.go.id/baca.php?berita=19. Retrieved 21 Nov 2010.
- ^ = "Regional Economy-West Nusa Teggara provincial profile". http://www.bi.go.id/web/id/DIBI/Info_Publik/Ekonomi_Regional/Profil/NTB/Demografi.htm =. Retrieved 1 sept 2010.
- ^ "Taman Nasional Gunung Rinjani-Mount Rinjani National Park". Dephut.go.id. http://www.dephut.go.id/INFORMASI/TN%20INDO-ENGLISH/tn_rinjani.htm. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- ^ "''Indonesian language'' Mount Rinjani National Park proposed to be the world geopark by M.Roil Bilad, downloaded 26 Aug, 2010". Sasak.org. http://www.sasak.org/berita/pariwisata/1981-taman-nasional-gunung-rinjani-diusulkan-jadi-geopark-dunia.html. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- ^ Khafid, Supriyantho (25 August 2010). "Mount Rinjani National Park Proposed to Become World Geopark". TempoInteraktifcom. http://www.tempo.co.id/hg/nasional/2010/08/25/brk,20100825-273939,uk.html. Retrieved 2 Sept 2010.
- ^ [|Khafid, Supriyantho] (25 Aug 2010). "Press Release-Mount Rinjani National Park Proposed Become World Geopark". NTB Regional Government. http://ntbprov.go.id/. Retrieved 2 Sept 2010.
- ^ "SINGGASANA Hotels and Resorts". Singgasanahotels.com. http://www.singgasanahotels.com/prg/golf.htm. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- ^ "Facilities". Medana Bay Marina. http://www.medanabaymarina.com/facilities.html. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- ^ "Sail Indonesia". Sail Indonesia. 2010-09-30. http://www.sailindonesia.net/home/home.php. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- ^ "Sail Indonesia-Sail Indonesia 2011 Rally Routes". Sail Indonesia. 2011-01-07. http://www.sailindonesia.net/home/home.php. Retrieved 2011-01-15.
Notes
Please see main Lombok article for more detail.
There are Four Regencies on the Island of Lombok.
External links
- Kabupaten Lombok Utara the Regency of North Lombok
- Kabupaten Lombok Tengah, the Regency of Central Lombok
- Kabupaten Lombok Timur, the Regency of East Lombok
- Kabupaten Lombok Barat, the Regency of West Lombok
- Nusa Teggara Barat, West Nusa Teggara
- Kota Mataram, City of Mataram
Regencies and cities of West Nusa Tenggara Capital: MataramRegencies
Bima • Dompu • West Lombok • Central Lombok • East Lombok • North Lombok • Sumbawa • West Sumbawa

Cities
Categories:- Regencies of West Nusa Tenggara
- Lombok
- West Nusa Tenggara
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.