- National Port Authority
-
National Port Authority of the Republic of Liberia Abbreviation NPA Formation 1921 Type Port district Headquarters Freeport of Monrovia
Bushrod Island, MonroviaRegion served Liberia Managing Director Matilda Parker Website Official Website  Current Managing Director Matilda Parker
Current Managing Director Matilda Parker
The National Port Authority of the Republic of Liberia (NPA) is the government agency responsible for the governance and operation of the ports of Liberia. Established in 1967, its main office is on Bushrod Island in Monrovia and the current Managing Director of the NPA is Hon. Matilda Parker.
On March 2010, the Freeport of Monrovia became ISPS Compliant (with no conditions) and moved from Security Level 2 to Security Level 1 in July 2010. The Freeport of Monrovia awarded Operations Contract to APM Terminal to handle port operations, which includes container handling, cargo handling, and marine.
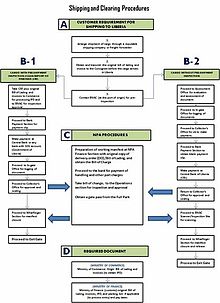
As of 2011, a One-Stop Shop has been established at the Port to make it expedite Shipping and Clearing Procedures. Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Commerce, and Central Bank have set up sub stations at the Port to expedite the process.
Contents
Establishment
An act of Legislature established the National Port Authority in 1967 (amended in 1970) as a state-owned enterprise to manage, plan and develop all ports in Liberia. The Authority manages four ports, namely, the Freeport of Monrovia, the Port of Buchanan, the Port of Greenville and the Port of Harper.
The Freeport of Monrovia is the largest in the Authority's Network. The United States Military built the port during World War II for strategic purposes. It handles most of the country's imported cargoes. Two breakwaters, 2,359m and 2,200m long, protect the harbour, enclosing a basin of 300 hectares of protected water. The general cargo berth, (the main pier), consists of an opened piled, 610m long by 11m wide marginal wharf with a reinforced concrete deck. The main wharf serves 2nd and 3rd generation coastal and mainline vessel.
The Port of Buchanan is located 170miles South-east of Monrovia. The Liberia-American Swedish Company (LAMCO), a joint venture company, constructed the port in 1960 for the export of iron ore deposits of the Nimba Range. Two break waters, 1,890m and 590m long to protect the harbour. Inside the basin, a 225m long ore-loading quay is located to the deeper section of the harbour basin with a water depth of 12.95m below chart datum. Adjacent to the loading quay, a waiting berth for ore carrier is available. On the inner side of the secondary breakwater, a commercial quay 334m long is located with an available water depth of 10.15m below chart datum. The access channel to the port provides ship a water depth of 14.95m below chart datum and a channel width between the breakwaters of 210m.
The Port of Greenville is also located in the South-eastern region of the country, Sinoe County, about 421 miles from the Freeport of Monrovia. A 400m long breakwater protects the harbour. There are two quays (70m and 180m long respectively) on the inner side of the breakwater for berthing facilities, with an existing water depth of 6m below chart datum. The port was rehabilatated in the early eighties with loan from the German Development Fund. The port functions mainly as an outlet for the timber industry.
The Port of Harper is situated in the South-eastern region of Liberia, Maryland County, near the border with the Ivory Coast, about 476 miles from the Freeport of Monrovia. The Port was constructed in 1959, on the rocky Russwurn Island, by connecting the island to the mainland with a causeway and by constructing a 150m long breakwater off the Russwurn Island. A 100m long reinforced concrete pier with an available water depth of 5.50m provides berthing facilities. The port serves the timber industry of the South-eastern hinterland.
Port of Monrovia
Main article: Freeport of MonroviaThe largest port in the authority's network, Freeport of Monrovia was built by the United States military during World War II for strategic purposes. It handles most of the authority's imported cargo, some of which are transshipped to other Liberian ports and to third countries. The Freeport of Monrovia consists of an artificial harbor formed by two-rock breakwater approximately 2,300 meters out into the open sea, which encompass some 300 hectares of protected water. The coastline between the breakwater is dredged to accommodate ocean going vessel and ore carriers (up to 100,000 dwt) and a marginal wharf of 610 meters long is capable of berthing 3-4 ships according to their size. The port is connected with Monrovia by an access road(four lanes approximately 1.5 kilometers long with two connecting bridges over the Mesurraddo River of which one is out of use.
From the seaside, the vessel enter the harbor basin through an entrance channel approximately 2,000 m long and 180 m wide. The central part of the port area is occupied by two iron ore companies (NIOC and Bong Mines) that previously operated their own facilities but have since folded up operations. A crude oil mooring station is located between the iron ore piers.
The general cargo wharf located south of this central area, is entirely operated by NPA which provides all onshore services and facilities to the users. The former Liberia Mining Company (LMC) pier which is not operational except for use by local fishing trawlers is situated at the northern end of the General Cargo wharf.
There is 500 m long oil jetty for refined products situated alongside the southern breakwater approximately 450 m off the coastline and it is connected to the tank farms by pipelines. The back of the Freeport is occupied by the port warehouses and shed s and also by private bonded warehouses.
Port of Buchanan
The Port of Buchanan is located some 272 kilometers South-East of Monrovia. It constructed in 1960 by the Liberian-American Swedish Mining Corporation (LAMCO), a joint venture company, to export the iron ore deposits of the Nimba range.
The Harbor is protected by two breakwaters, 1890 and 590 long respectively. Inside the basin, a 255 meters long ore loading quay is located adjacent to the deeper section of the harbor basin, providing a water depth of 12.95m below chart datum. Adjacent to the loading quay, a waiting berth for ore carriers is available. On the inner side of secondary breakwater, a commercial quay, 334 meters long is located with available water depth of 9.5 m.
Latitude: 5° 51' 29" N
Longitude: 10° 3' 15" W
UN/LOCODE: LRUCN
Port Type: Seaport
Port Size: Small
Port of Harper
It was constructed by connecting the Island to the mainland with a causeway and constructing a 150 meter long breakwater off Russwurm Island. Berthing facilities are provided by a 100 meter long reinforced concrete pier with available water depth of 5.5 meters on both sides. Its activities are centered on the exports of logs and sawn timber from the southeastern hinterland of the country. It has the potential to handle traffic that will derive from the reactivation of the palm oil sector.
Latitude: 4° 22' 18" N
Longitude: 7° 43' 25" W
UN/LOCODE: LRHAR
Port Type: Pier, Jetty or Wharf
Port Size: Small
Port of Greenville
The Port of Greenville is located in the south-eastern region of the country, about 673 kilometers from the Freeport of Monrovia. The harbor is protected by a 400 meter long two quay breakwater on the inner side. There are two berthing facilities 70 and 80 meters long respectively, with existing water depth of 6 meters below chart datum.
It was rehabilitated in the early 1980s with funds from the German Development Fund. Prior to the civil crisis, the port functioned as an outlet for the log and sawn timber industries. It had an annual pre-war throughput of 281,860.5 metric tons.
Latitude: 4° 59' 22" N
Longitude: 9° 2' 30" W
UN/LOCODE: LRGRE
Port Type: Harbor
Port Size: Small
See also
References
External links
Categories:- Government of Liberia
- Port authorities
- Organizations established in 1967
- Monrovia
- Ports and harbours of Liberia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.