- European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity
-
European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity 
Abbreviation ENTSO-E Predecessor ETSO, UCTE, NORDEL, ATSOI, UKTSOA, BALTSO Formation 19 December 2008 Type association Purpose/focus to promote important aspects of energy policy in the face of significant challenges Headquarters Avenue de Cortenbergh 100 Location Brussels, Belgium Region served Europe Membership transmission system operators Secretary General Konstantin Staschus President Daniel Dobbeni Vice President Jukka Ruusunen Chairman of the Board Graeme Steele Main organ Assembly Website www.entsoe.eu The European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E) is an association of Europe's transmission system operators (TSOs) for electricity. It is a successor of ETSO, the association of European transmission system operators founded in 1999 in response to the emergence of the internal electricity market within the European Union.
Contents
History
On 27 June 2008, 36 European electricity transmission system operators (TSO) signed in Prague a declaration of intent to create the ENTSO-E.[1] The ENTSO-E was established on 19 December 2008 in Brussels by 42 TSOs as a successor of six regional associations of the electricity transmission system operators.[2][3] The ENTSO-E became operational on 1 July 2009. The former associations ETSO, ATSOI, UKTSOA, NORDEL, UCTE and BALTSO became a part of the ENTSO-E, while still offering data by their predecessors for public interest.[4]
Objectives
Creation of the ENTSO-E was initiated by the adoption of the European Union third legislative package on the gas and electricity markets.[1] In 2003, the European Commission conducted a sector inquiry concerning the competition of electricity market in six European countries.[5] Examining competition in these countries, the final report stated serious issues to be solved.[6] It was noticed that the integration between member state's markets is still insufficient. Additionally, the absence of transparently available market information was assessed.[5] As a result, the third legislative package on the EU gas and electricity markets was adopted by the European Commission in September 2007.[7]
Main tasks
- Elaboration and establishment of network codes[8]
- Ensure coordination of network operation by common network operation tools[9]
- Develop a ten-year network development plan[10]
- Publish annual work programme, annual report and annual summer and winter generation adequacy outlooks[11]
Objectives
- Security of supply[12][13]
- Meeting the needs of the Internal Energy Market and facilitating market integration[14]
- Promotion of relevant R&D and the public acceptability of transmission infrastructure[14]
- Consultation with Stakeholders and positions towards energy policy issues[14]
Members
The ENTSO-E now contains 42 TSOs from 34 countries, which now share an interconnected transmission grid in the EU.[15]
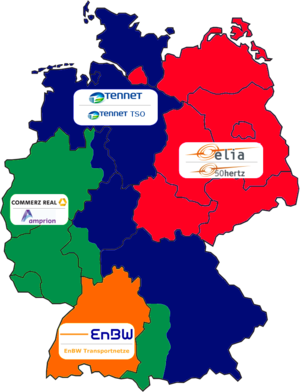
ISO country code Country TSO Abbr. AT Austria TIWAG Netz ??? AT Austria Verbund - Austrian Power Grid APG AT Austria VKW-Netz BE Belgium Elia System Operator BS Bosnia Herzegovina ISO BiH BG Bulgaria Electroenergien Sistemen Operator HR Croatia Hrvatska elektroprivreda HEP-OPS CY Cyprus Cyprus Transmission System Operator Cyprus TSO CZ Czech Republic ČEPS DK Denmark Energinet.dk EE Estonia Elering FI Finland Fingrid FR France Réseau de Transport d'Électricité RTE DE Germany EnBW Transportnetze EnBW TNG DE Germany Tennet TSO TTG DE Germany Amprion DE Germany 50Hertz Transmission 50Hertz GR Greece Hellenic Transmission System Operator HTSO HU Hungary MAVIR IS Iceland Landsnet IE Ireland EirGrid IT Italy Terna LV Latvia Augstsprieguma tïkls LT Lithuania Litgrid LU Luxembourg Creos Luxembourg MK Republic of Macedonia MEPSO ME Montenegro AD Prenos NL Netherlands TenneT NO Norway Statnett PL Poland PSE-Operator PT Portugal Redes Energéticas Nacionais REN RO Romania Transelectrica RS Serbia JP Elektromreža Srbije SK Slovak Republic SEPS SI Slovenia Elektro-Slovenija ELES ES Spain Red Eléctrica de España REE SE Sweden Svenska Kraftnät CH Switzerland swissgrid GB United Kingdom National Grid plc National Grid GB United Kingdom System Operator for Northern Ireland SONI GB United Kingdom Scottish and Southern Energy SSE GB United Kingdom Scottish Power Transmission plc SPTransmission Regional structure
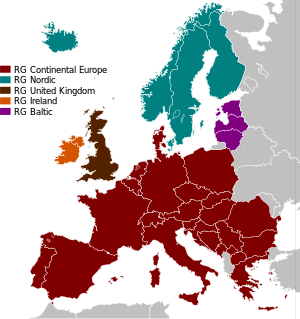
ENTSO-E is divided into five regional groups, which derive from the historic background of the former associations.
Continental Europe
The regional group of Continental Europe includes the members of the former Union for the Co-ordination of Transmission of Electricity (UCTE). The UCTE was founded in 1951 as the Union for the Coordination of Production and Transmission of Electricity consisting of an interconnected companies from Switzerland, France and Germany. Over the time, most of TSOs of Continental Europe joined the association. In 1999, UCTE re-defined itself as an association of TSOs. Before merging to ENTSO-E, UCTE represented 29 transmission system operators of 24 countries operating the synchronous grid of Continental Europe.[16]
Ireland
The region of Ireland consists of EirGrid and System Operator for Northern Ireland (SONI), the members of the former Association of the Transmission System Operators of Ireland (ATSOI).[17]
United Kingdom
The region of the United Kingdom consists of the TSOs of the United Kingdom, a members of the UK Transmission System Operators Association (UKTSOA).[18]
Nordic
The Nordic region consists of Finland, Sweden, Norway and Eastern Denmark, the members of the former Nordic TSO association NORDEL. NORDEL was founded in 1963 for co-operation between the TSOs of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden for a further development of an harmonized Nordic electricity market.[19]
Baltic
The Baltic region consists of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. Before creation of the ENTSO-E, the Baltic TSOs were members of the Baltic Transmission System Operators association (BALTSO). BALTSO was founded on 30 March 2006.[20]
Frequency
In order to ensure a working European power grid, the operating frequency is defined by a standard of 50 hertz. As electric generation and consumption differs, the power transmission grid has to be balanced. There should be the same amount of input and output. Nevertheless changes in the frequency may occur if supply or demand exceeds its counterpart. In case of too much supply the frequency will increase, while in case of too much demand it will decrease. The main task is to keep the frequencies of all five synchronous areas balanced around the 50 hertz standard to ensure a safe power supply.[21]
Electronic data interchange
An open European electricity market needs a considerable electronic data interchange between all market participants in order to improve the coordination between different inter-country systems. The aim of the ENTSO-E is to offer all participants the necessary information of the existing EDI standards and their specifications. In association with ebiX and EFET (European Federation of Energy Traders) ENTSO-E maintains a Harmonised role model for the European electricity market.[22]
System development
The ENTSO-E will publish a ten-year network development statement, which ought to ensure the reliability and security of electric energy supply in Europe. An adequate grid should be available for the functioning of the European electricity market. The committee will introduce technical rules and standards related to the planning of transmission systems and new technical concepts within R&D-activities. Furthermore it will focus on facilitating the exchange of information about efficient asset management, system technology and critical infrastructure protection among members. In order to fulfill its duties and tasks, the committee will investigate and develop long-term and medium-term system extension strategies, draw system studies and collect data relevant for system development.[23]
See also
- EURELECTRIC
- Agency for the Cooperation of Energy Regulators
- European Energy Community
- European Network of Transmission System Operators for Gas (ENTSOG)
- IPS/UPS – TSO organization for the networks of most of the former Soviet republics and Mongolia
- SuperSmart Grid, European super grid
Notes
- ^ a b "TSOs for electricity are founding new association" (Press release). ENTSO-E. 1 July 2008. http://www.entsoe.eu/index.php?id=42&tx_ttnews%5BpS%5D=1260881300&tx_ttnews%5Bpointer%5D=3&tx_ttnews%5Btt_news%5D=25&tx_ttnews%5BbackPid%5D=214&cHash=c14bdb7c51. Retrieved 17 January 2010.
- ^ "TSOs for electricity have founded a new association" (Press release). ENTSO-E. 19 December 2008. http://www.entsoe.eu/index.php?id=42&tx_ttnews%5BpS%5D=1260881300&tx_ttnews%5Bpointer%5D=3&tx_ttnews%5Btt_news%5D=24&tx_ttnews%5BbackPid%5D=214&cHash=43195ba1dc. Retrieved 17 January 2010.
- ^ "European TSOs established new organisation ENTSO-E" (Press release). Statnett. 19 December 2008. http://www.statnett.no/en/News/News-archive-Temp/News-archive-2008/European-TSOs-established-new-organisation-ENTSO-E/. Retrieved 17 January 2010.
- ^ "ENTSO-E, fully operational as of 1 July, welcomes the adoption of the EU's 3rd energy package" (Press release). ENTSO-E. 1 July 2009. http://www.entsoe.eu/index.php?id=42&tx_ttnews%5Btt_news%5D=6&tx_ttnews%5BbackPid%5D=43&cHash=e16118187a. Retrieved 17 January 2010.
- ^ a b "Inquiry pursuant to Article 17 of Regulation (EC) No 1/2003". European Commission. 2005. http://ec.europa.eu/competition/sectors/energy/inquiry/index.html. Retrieved 17 January 2010.
- ^ "Communication from the Commission – Inquiry pursuant to Article 17 of Regulation (EC) No 1/2003 into the European gas and electricity sectors". European Commission. 2007. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:52006DC0851:EN:NOT. Retrieved 12 March 2010.
- ^ "Energising Europe – a real market with secure supply (Third legislative package)". European Commission. http://ec.europa.eu/energy/gas_electricity/third_legislative_package_en.htm. Retrieved 17 January 2010.
- ^ The European Parliament and Council (2009):, Regulation (EC) No. 714/2009, Article 6–8, http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32009R0714:EN:NOT
- ^ The European Parliament and Council (2009):, Regulation (EC) No. 714/2009, Article 8 (3a), http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32009R0714:EN:NOT
- ^ The European Parliament and Council (2009):, Regulation (EC) No. 714/2009, Article 8 (3b), http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32009R0714:EN:NOT
- ^ The European Parliament and Council (2009):, Regulation (EC) No. 714/2009, Article 8 (3d-f), http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32009R0714:EN:NOT
- ^ The European Parliament and Council (2009):, Regulation (EC) No. 714/2009, Article 1', http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32009R0714:EN:NOT
- ^ European Network of Transmission System Operators (2009): Mission, http://www.entsoe.eu/index.php?id=14
- ^ a b c The European Parliament and Council (2009):, Regulation (EC) No. 714/2009, Article 1, http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32009R0714:EN:NOT
- ^ European Network of Transmission System Operators (2009): ENTSO-E Member Companies, http://www.entsoe.eu/index.php?id=15
- ^ European Network of Transmission System Operators (2009): UCTE – Union for the Coordination of the Transmission of Electricity,http://www.entsoe.eu/index.php?id=102
- ^ European Network of Transmission System Operators (2009): ATSOI – Association of the Transmission System Operators of Ireland, http://www.entsoe.eu/index.php?id=98
- ^ European Network of Transmission System Operators (2009): UKTSOA – UK Transmission System Operators Association, http://www.entsoe.eu/index.php?id=103
- ^ European Network of Transmission System Operators (2009): Nordel, http://www.entsoe.eu/index.php?id=101
- ^ European Network of Transmission System Operators (2009): BALTSO – Baltic Transmission System Operators, http://www.entsoe.eu/index.php?id=99
- ^ European Network of Transmission System Operators (2009): 50 Hertz: a delicate balance, http://www.entsoe.eu/index.php?id=108
- ^ European Network of Transmission System Operators (2009): Electronic Data Interchange, http://www.entsoe.eu/index.php?id=105
- ^ European Network of Transmission System Operators (2009): System Development, http://www.entsoe.eu/index.php?id=22
External links
Categories:- Electric power transmission system operators
- Electric power in the European Union
- International energy organizations
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.