- Ubenimex
-
Ubenimex[1] 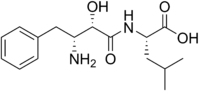 (2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-3-Amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoic acidOther namesBestatin; N-[(2S,3R)-3-Amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutyryl]-L-leucine
(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-3-Amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoic acidOther namesBestatin; N-[(2S,3R)-3-Amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutyryl]-L-leucineIdentifiers CAS number 58970-76-6,
65391-42-6 (HCl)PubChem 72172 ChEMBL CHEMBL29292 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC(C)C[C@@H](C(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](CC1=CC=CC=C1)N)O
Properties Molecular formula C16H24N2O4 Molar mass 308.37 g mol−1 Melting point 245 °C (dec.)
Hazards S-phrases S22 S24/25  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Ubenimex (INN), also known as bestatin, is a competitive protease inhibitor. It is an inhibitor of aminopeptidase B[2], leukotriene A4 hydrolase [3], aminopeptidase N.[4] It is being studied for use in the treatment of acute myelocytic leukemia.[5]
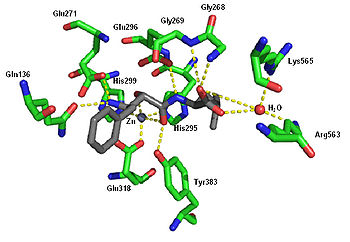 Crystal structure of bestatin in the binding pocket of leukotriene A4 hydrolase. Rendered from PDB 1HS6.
Crystal structure of bestatin in the binding pocket of leukotriene A4 hydrolase. Rendered from PDB 1HS6.
References
- ^ N-((2S,3R)-3-Amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutyryl)-L-leucine at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ Umezawa,H., Aoyagi,T., Suda,H., Hamada,M. & Takeuchi,T. (1976). Bestatin, an inhibitor of aminopeptidase B, produced by actinomycetes.. pp. 97–99.
- ^ Muskardin,D.T., Voelkel,N.F. & Fitzpatrick,F.A. (1994). Modulation of pulmonary leukotriene formation and perfusion pressure by bestatin, an inhibitor of leukotriene A4 hydrolase.. pp. 131–137.
- ^ K Sekine, H Fujii and F Abe (1999). Induction of apoptosis by bestatin (ubenimex) in human leukemic cell lines. 13. pp. 729–734.
- ^ Hirayama, Y; Sakamaki, S; Takayanagi, N; Tsuji, Y; Sagawa, T; Chiba, H; Matsunaga, T; Niitsu, Y (2003). "Chemotherapy with ubenimex corresponding to patient age and organ disorder for 18 cases of acute myelogeneous leukemia in elderly patients--effects, complications and long-term survival". Gan to kagaku ryoho. Cancer & chemotherapy 30 (8): 1113–8. PMID 12938265.

This pharmacology-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
