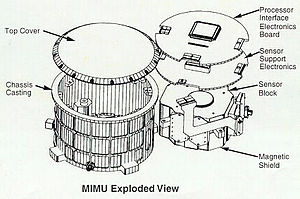
- Miniature inertial measurement unit (MIMU)
-
Miniature inertial measurement unit (MIMU) is an inertial measurement unit (IMU) developed and built by Honeywell International[citation needed] to control and stabilize spacecraft during mission operations. MIMUs can also be configured to perform as an inertial reference unit (IRU). MIMUs have been flown on GEO, Low Earth orbit (LEO), planetary missions and deep-space-probe applications.
Contents
Missions
Geostationary (GEO) missions
Low-Earth orbiting (LEO) Missions
Planetary missions
- Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter[1] – launched in 2005 on a mission to study the planet Mars
- STEREO[2] – launched in 2006 on a mission to study the Sun
- Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter[3] – launched in 2009 on a mission to study the Moon
Deep-space-probe missions
- New Horizons – launched in 2006 on a mission to study the planet Pluto
Notes and references
- ^ "Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Design Approach for High-Resolution Surface Imaging". PDF. American Astronautical Society. http://trs-new.jpl.nasa.gov/dspace/bitstream/2014/37230/1/03-0246.pdf. Retrieved 2006-07-29.
- ^ "Honeywell To Provide Miniature Inertial Measurement Units For STEREO Spacecraft". Web. Honeywell International, Inc.. http://www.honeywell.com/en/aerospace/announcement_details.jsp?rowID=115&docID=3995&catID=2. Retrieved 2006-10-25.[dead link]
- ^ "NASA GSFC Solicitation: Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Intertial (LRO) Reference Unit (IRU)". Web. Moon Today. http://www.moontoday.net/news/viewsr.html?pid=19234. Retrieved 2006-11-01.
External links
Categories:- Technology stubs
- Navigation
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.