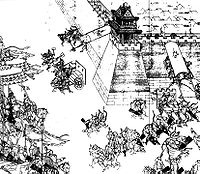
- Manchu Conquest
-
Manchu Conquest 
Qing Dynasty in 1820.Date 1618-1696 Location Manchuria and China Result Ming Dynasty falls
Qing Dynasty is formedBelligerents Manchus Ming Dynasty Commanders and leaders Nurhaci
Dodo
DorgonChongzhen Emperor
Yuan ChonghuanCasualties and losses varies varies The Manchu Conquest was a long period of war between the Manchus from the north and the Ming Dynasty in the south. The Manchus conquered Korea and Manchuria, heading south to conquer the Ming. General Wu Sangui, among others, defected to the Manchu and led to the fall of Beijing. Soon after, the Kangxi Emperor ascended the throne and fought off several rebellions and then countered by launching a series of campaigns that expanded his empire.
Contents
Fall of the Ming
Main article: Fall of the Ming DynastyJurchen expansion
Jurchen warlord Nurhaci is retrospectively identified as the founder of the Qing dynasty. In 1616 he declared himself khagan. His unifying efforts gave the Jurchen the strength to assert themselves. In 1618 he proclaimed Seven Grievances against the Ming and seized the city of Fushun in what is now Liaoning province in China's northeast. In a series of successful military campaigns in Liaodong and Liaoxi (east and west of the Liao River), the Jurchens seized a number of Ming cities including Shenyang, which they made into the capital of their newly founded "Later Jin" dynasty, named after a Jurchen polity that had ruled over north China several centuries earlier.
Under the inspirational leader Yuan Chonghuan, the Ming used western artillery to defeat the Jin forces at the Battle of Ningyuan in 1626. Nurhaci was injured and died soon afterwards, but the Ming failed to seize the chance to counter-attack. The Jurchens' nemesis Yuan Chonghuan was soon purged in a political struggle, while under the leadership of the new khan Hung Taiji the Jurchens kept seizing Ming cities, defeated Joseon Korea, a crucial ally of the Ming, in 1627 and 1636, and raided deep into China in 1642 and 1643.
Rebellions
 Wu Sangui was a general of the Ming Dynasty, who later defected to the Qing Dynasty. However, his hopes to restore the former were dashed and rebelled against the Kangxi Emperor.
Wu Sangui was a general of the Ming Dynasty, who later defected to the Qing Dynasty. However, his hopes to restore the former were dashed and rebelled against the Kangxi Emperor.
The Ming faced several famines, floods, economic chaos, and rebellions. Li Zicheng rebelled in the 1630s in Shaanxi in the north, while a mutiny led by Zhang Xianzhong broke out in Sichuan in the 1640s. Many people were killed in this self-proclaimed emperor's reign of terror. In 1642 Ming forces besieged Kaifeng and over 300,000 people died.[citation needed] In 1644, at last, Li's forces entered Beijing. The Chongzhen Emperor committed suicide.
The conquest
After the fall of Beijing to Li Zicheng, Ming commander Wu Sangui still hoped he could restore the Ming, but was soon cornered by Li Zicheng. He turned to the Manchus, and defeated Li Zicheng's forces at the Battle of Shanhai Pass with their help. But he effectively invited a Manchu invasion of the rest of China.
The order to make new subjects shave their front hair and wear a pigtail was a profound humilitation for the populace. In 1645, the city of Yangzhou in Jiangsu was the scene of a massacre in which thousands died at Dodo's hands.
A man known as Koxinga established his own state in Xiamen. His armies founded alliances with nearby powers against the Manchu, but was driven back to the sea. So he gathered a navy and conquered Taiwan from the Dutch. He founded the Kingdom of Tungning in the island, a base of operations against the Manchu. However, he died the same year of his great feat. This ended any idea of a Ming restoration, but the Manchu faced opposition from its inside.
Wu Sangui, Shang Kexi, and Geng Jimao, the "Three Feudatories", rebelled against the Kangxi Emperor. They dominated southern China, and Wu declared the "Zhou Dynasty". However, their disunity destroyed them. Shang Zhixin and Geng surrendered in 1681 after a massive Qing counteroffensive.
Rise of Emperor Kangxi
The Kangxi Emperor, the one who had crushed the Three Feudatories' revolt, began his own campaigns to expand his empire. In 1683 he dispatched Shi Lang with a fleet of 300 ships to take Taiwan in 1683 from the wealthy Zheng family. The descendants of Koxinga did not stand a chance against the experienced Manchu troops. He used the Zheng family's knowledge of sea warfare to seize the town of Albazin on the Amur River from Russia in 1685, giving the Manchus control of all the area south of the river.
Finally, Kangxi gambled on an invasion of the north. Galdan, leader of the Zunghar Khanate, prepared to unite the tribes of Mongolia to restore the Mongol Empire. The Chinese armies of 80,000 led by the Emperor Kangxi himself marched south of Ulaanbaatar to engage the Zunghars. In a brief engagement, the enemy units were pounded by cannon fire and routed. Galdan died one year later.
Aftermath
Kangxi's conquest of Mongolia completed his northern expedition. Before his death in 1722, he expanded his empire as far as the Tibetan capital of Lhasa. His successors campaigned further, taking over areas of southeast Asia, Persia, Nepal, and the Indian subcontinent. In 1710, he orchestrated the standard Kangxi dictionary and gave a written language for Manchu.
The Qing Dynasty would rule until the Wuchang Uprising in 1911. Puyi, the last reigning Manchu emperor, officially abdicated the following year. The Qing empire laid the territorial foundation for the modern-day People's Republic of China.
References
- Saul, David War: A Definitive Visual History
- Grant, RG Battle
- Grant, RG Commander
Categories:- Wars involving Qing Dynasty
- History of Manchuria
- History of Mongolia
- History of China
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.