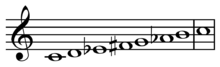- Neapolitan scale
-
In music, the major Neapolitan scale and the minor Neapolitan scale are two musical scales, one minor, one major.
The sequence of scale steps Neapolitan minor is as follows[1]:
1 b2 b3 4 5 b6 7 8 A Bb C D E F G# A [ h w w w h A h C Db Eb F G Ab B C]
And for Neapolitan major[1]:
1 b2 b3 4 5 6 7 8 A Bb C D E F# G# A [ h w w w w w h C Db Eb F G A B C]
Thus the scales are distinguished from the harmonic and ascending melodic minor scales by the flattened supertonic or second scale degree.
Both are accompanied well by power or minor chords[1].
Neapolitan minor may also be called or refer to the Hungarian Gypsy scale and Neapolitan major may also be called or Lydian major scale[3].
See also
Sources
- ^ a b c Celentano, Dave (1991). Monster Scales and Modes, p.44. Published by CentreStream. ISBN 0931759595.
- ^ Cooper, Paul (1973). Perspectives in Music Theory: An Historical-Analytical Approach, p.18. ISBN 0-396-06752-2.
- ^ Kadmon, Adam (1998). The Guitar Grimoire Progressions & Improvisation, p.280. ISBN 0825831970.
Musical scales Main Western Types Bebop · Diatonic · Enharmonic · Jazz · Synthetic
Name Acoustic · Alpha scale · Altered · Beta scale · Blues · Bohlen-Pierce · Double harmonic · Enigmatic · Gamma scale · Half diminished · Harmonic major · Harmonic Scale · Lydian dominant · Major locrian · Misheberak · Phrygian dominant · Whole tone
Ethnic origin Algerian · Arabic (Double harmonic • Major locrian • Quarter tone • 17 equal temperament) · Gamelan pelog · Gamelan slendro · Gypsy · Hungarian gypsy · Hungarian minor · Neapolitan minor and major · Persian · Ukrainian minor · Yo · In
Modes Modes in Western music Gregorian Other Diatonic Minor Melodic minor (I) · Dorian ♭2 (II) · Lydian Augmented (III) · Lydian Dominant (IV) · Mixolydian ♭13 (V) · Locrian ♮2 (VI) · Altered (VII)See also Properties of musical modesNumber of tones Pentatonic · Hexatonic · Heptatonic · Octatonic · Chromatic
Categories:- Music stubs
- Scales with unusual key signatures
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.