- Diamond graph
-
Diamond graph 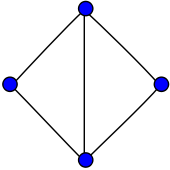
Vertices 4 Edges 5 Radius 1 Diameter 2 Girth 3 Automorphisms 4 (Z/2Z×Z/2Z) Chromatic number 3 Chromatic index 3 Properties Hamiltonian
Planar
Unit distancev · mathematical field of graph theory, the diamond graph is a planar undirected graph with 4 vertices and 5 edges.[1][2] It consists of a complete graph K4 minus one edge. The diamond Graph has radius 1, diameter 2, girth 3, chromatic number 3 and chromatic index 3. It is also a 3-vertex-connected and a 3-edge-connected graceful[3] Hamiltonian graph.
Diamond-free graphs and forbidden minor
A graph is diamond-free if it has no diamond as an induced subgraph. The triangle-free graphs are diamond-free graphs, since every diamond contains a triangle. The Hougardy's conjecture is proved for diamond-free graphs.[4]
The family of graphs in which each connected component is a cactus graph is downwardly closed under graph minor operations. This graph family may be characterized by a single forbidden minor. This minor is the diamond graph.[5]
If both the butterfly graph and the diamond graph are forbidden minors, the family of graphs obtained is the family of pseudoforests.
Algebraic properties
The full automorphism group of the diamond graph is a group of order 4 isomorphic to the Klein four-group, the direct product of the cyclic group Z/2Z with itself.
The characteristic polynomial of the diamond graph is x(x + 1)(x2 − x − 4). It is the only graph with this characteristic polynomial, making it a graph determined by its spectrum.
References
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W., "Diamond Graph" from MathWorld.
- ^ ISGCI: Information System on Graph Class Inclusions v2.0. "List of Small Graphs".
- ^ Sin-Min Lee, Y.C. Pan and Ming-Chen Tsai. "On Vertex-graceful (p,p+l)-Graphs". [1]
- ^ Kezdy A.E, Scobee M. "A proof of Hougardy's conjecture for diamond-free graphs". Discrete Mathematics, Volume 240, 1, 28 septembre 2001, pp. 83-95(13).
- ^ El-Mallah, Ehab; Colbourn, Charles J. (1988), "The complexity of some edge deletion problems", IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems 35 (3): 354–362, doi:10.1109/31.1748 .
Categories:- Individual graphs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Diamond cubic — Unit cell of the diamond cubic crystal structure … Wikipedia
Matchstick graph — The Harborth Graph In geometric graph theory, a branch of mathematics, a matchstick graph is a graph that can be drawn in the plane in such a way that its edges are line segments with length one that do not cross each other. That is, it is a… … Wikipedia
Cactus graph — A cactus graph (sometimes called a cactus tree) is a connected graph in which any two simple cycles have at most one vertex in common. Equivalently, every edge in such a graph may belong to at most one cycle.Cactus graphs were first studied under … Wikipedia
Periodic graph (crystallography) — For other uses, see Periodic graph. A (large) unit cell of Diamond crystal net; the balls represent carbon atoms and the sticks represent covalent bonds … Wikipedia
Line graph of a hypergraph — The line graph of a hypergraph is the graph whose vertex set is the set of the hyperedges of the hypergraph, with two edges adjacent when they have nonempty intersection. In other words, the line graph of a hypergraph is the intersection graph of … Wikipedia
Propositional directed acyclic graph — A propositional directed acyclic graph (PDAG) is a data structure that is used to represent a Boolean function. A Boolean function can be represented as a rooted, directed acyclic graph of the following form: * Leaves are labeled with op (true),… … Wikipedia
Pseudoforest — A 1 forest (a maximal pseudoforest), formed by three 1 trees In graph theory, a pseudoforest is an undirected graph[1] in which every connected component has at most one cycle. That is, it is a system of vertices and edges connecting pairs of ve … Wikipedia
Tutte polynomial — This article is about the Tutte polynomial of a graph. For the Tutte polynomial of a matroid, see Matroid. The polynomial x4 + x3 + x2y is the Tutte polynomial of the Bull graph. The red line shows the intersection with the plane … Wikipedia
Graphe diamant — Représentation du graphe diamant. Nombre de sommets 4 Nombre d arêtes 5 Distribution des degrés 2 (2 sommets) 3 (2 sommets) Rayon 1 … Wikipédia en Français
Logarithm — The graph of the logarithm to base 2 crosses the x axis (horizontal axis) at 1 and passes through the points with coordinates (2, 1), (4, 2), and (8, 3) … Wikipedia
18+© Academic, 2000-2024- Contact us: Technical Support, Advertising
Dictionaries export, created on PHP, Joomla, Drupal, WordPress, MODx.Share the article and excerpts
Diamond graph
- Diamond graph
-
Diamond graph 
Vertices 4 Edges 5 Radius 1 Diameter 2 Girth 3 Automorphisms 4 (Z/2Z×Z/2Z) Chromatic number 3 Chromatic index 3 Properties Hamiltonian
Planar
Unit distance
