- Pinus elliottii
-
Pinus elliottii 
Slash Pine plantation Conservation status Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae Division: Pinophyta Class: Pinopsida Order: Pinales Family: Pinaceae Genus: Pinus Subgenus: Pinus Species: P. elliottii Binomial name Pinus elliottii
Engelm.Varieties Pinus elliottii var. elliotti
Pinus elliottii var. densa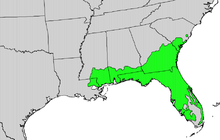
Pinus elliottii, commonly known as the Slash Pine, is a pine native to the southeastern United States, from southern South Carolina west to southeastern Louisiana, and south to the Florida Keys.[2]
It is fast-growing, but not very long-lived by pine standards (to 200 years), and prefers humid climates and moist soil.
Slash Pine is named after the "slashes" – swampy ground overgrown with trees and bushes – that constitute its habitat.
This tree reaches heights of 18–30 m (59–98 ft) with a trunk diameter of 0.6–0.8 m (2.0–2.6 ft). The leaves are needle-like, very slender, in clusters of two or three, and are 18–24 cm (7.1–9.4 in) long.
The cones are glossy red-brown, 5–15 cm (2.0–5.9 in) in length with a short (2–3 mm/0.079–0.12 in), thick prickle on each scale. It is known for its conical shape.
It may be distinguished from the related Loblolly Pine by the somewhat longer, glossier needles and larger red-brown cones, and from Longleaf Pine by the shorter, more slender needles and smaller cones with less broad scales.
There are two varieties:
- P. elliottii var. elliotti (typical Slash Pine). South Carolina to Louisiana, south to central Florida. Leaves in bundles (fascicles) of twos and threes, mostly threes. Cones larger, 7–15 cm (2.8–5.9 in).
- P. elliotti var. densa (South Florida Slash Pine or Dade County Pine). Pine rocklands of Southern Florida and Florida Keys, including the Everglades.[3][4] Leaves nearly all in bundles of two. Cones smaller, 5–12 cm (2.0–4.7 in).
Unlike the typical variety of Slash Pine, seedlings of P. elliotti var. densa pass through a "grass stage", in a manner similar to Longleaf Pine.
The Slash Pine also is known as the Yellow Slash Pine, Swamp Pine, and Pitch Pine, although it should not be confused with the tree more usually called the Pitch Pine, Pinus rigida.
This tree is widely grown in plantations, and also is used in horticulture.
References
- ^ Conifer Specialist Group (1998). Pinus elliottii. 2006. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN 2006. www.iucnredlist.org. Retrieved on 10 May 2006.
- ^ Moore, Gerry; Kershner, Bruce; Craig Tufts; Daniel Mathews; Gil Nelson; Spellenberg, Richard; Thieret, John W.; Terry Purinton; Block, Andrew (2008). National Wildlife Federation Field Guide to Trees of North America. New York: Sterling. p. 74. ISBN 1-4027-3875-7.
- ^ "Pine Rocklands" (PDF). United States Fish and Wildlife Service. http://www.fws.gov/southeast/vbpdfs/commun/pr.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-17.
- ^ Gilman, Edward F.; Dennis G. Watson (2006). "Pinus elliotti: Slash Pine". University of Florida, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences. http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/st463. Retrieved 12 April 2011.
External links
 Media related to Pinus elliottii at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Pinus elliottii at Wikimedia Commons  Data related to Pinus elliottii at WikispeciesCategories:
Data related to Pinus elliottii at WikispeciesCategories:- IUCN Red List least concern species
- Pinus
- Trees of Alabama
- Trees of Florida
- Trees of Georgia (U.S. state)
- Trees of Louisiana
- Trees of Mississippi
- Trees of South Carolina
- Trees of the Southeastern United States
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.