- DEFA6
-
Defensin, alpha 6, Paneth cell-specific 
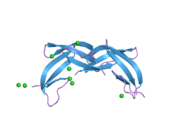
PDB rendering based on 1zmq.Available structures PDB 1zmq Identifiers Symbols DEFA6; DEF6; HD-6 External IDs OMIM: 600471 MGI: 99582 GeneCards: DEFA6 Gene Gene Ontology Cellular component • extracellular region
• extracellular spaceBiological process • killing of cells of other organism
• defense response to bacterium
• defense response to fungusSources: Amigo / QuickGO Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 1671 n/a Ensembl ENSG00000164822 n/a UniProt Q01524 n/a RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001926 n/a RefSeq (protein) NP_001917 n/a Location (UCSC) Chr 8:
6.78 – 6.78 Mbn/a PubMed search [1] n/a Defensin, alpha 6 (DEFA6) also known as human alpha defensin 6 (HD6) is a human protein that is encoded by the DEFA6 gene.[1][2] DEFA6 is expressed in the Paneth cells of the ileum.[3]
Function
The alpha defensins are a family of microbicidal and cytotoxic peptides that defend the host against bacteria and viruses. HD6 was reported to possess poor antibacterial potency.[4]
Several alpha defensin genes, including DEFA6, are clustered on chromosome 8.[1]
References
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: DEFA6 defensin, alpha 6, Paneth cell-specific (Homo sapiens)". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=DEFa6.
- ^ Jones DE, Bevins CL (January 1993). "Defensin-6 mRNA in human Paneth cells: implications for antimicrobial peptides in host defense of the human bowel". FEBS Lett. 315 (2): 187–92. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(93)81160-2. PMID 8417977.
- ^ Zhao C, Wang I, Lehrer RI (24 Nov 1996). "Widespread expression of beta-defensin hBD-1 in human secretory glands and epithelial cells". FEBS Lett 396 (2-3): 319–22. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(96)01123-4. PMID 8915011.
- ^ Ericksen B, Wu Z, Lu W, Lehrer RI. (2005). "Antibacterial activity and specificity of the six human alpha defensins.". Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 49 (1): 269–75. doi:10.1128/AAC.49.1.269-275.2005. PMC 538877. PMID 15616305. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=538877.
Further reading
- Szyk A, Wu Z, Tucker K, et al. (2006). "Crystal structures of human alpha-defensins HNP4, HD5, and HD6.". Protein Sci. 15 (12): 2749–60. doi:10.1110/ps.062336606. PMC 2242434. PMID 17088326. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2242434.
- Wu Z, Ericksen B, Tucker K, et al. (2004). "Synthesis and characterization of human alpha-defensins 4-6.". J Pept Res. 64 (3): 118–25. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3011.2004.00179.x. PMID 15317502.
- Mallow EB, Harris A, Salzman N, et al. (1996). "Human enteric defensins. Gene structure and developmental expression.". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (8): 4038–45. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.8.4038. PMID 8626737.
- Bevins CL, Jones DE, Dutra A, et al. (1996). "Human enteric defensin genes: chromosomal map position and a model for possible evolutionary relationships.". Genomics 31 (1): 95–106. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0014. PMID 8808285.
- Eisenhauer PB, Harwig SS, Lehrer RI (September 1992). "Cryptdins: antimicrobial defensins of the murine small intestine". Infect. Immun. 60 (9): 3556–65. PMC 257361. PMID 1500163. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=257361.
- Huttner KM, Selsted ME, Ouellette AJ (February 1994). "Structure and diversity of the murine cryptdin gene family". Genomics 19 (3): 448–53. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1093. PMID 8188287.
PDB gallery Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 8 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.