- Apiose
-
Apiose 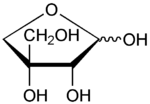 2,3,4-trihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)butanalOther namesD-apiose
2,3,4-trihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)butanalOther namesD-apiose
3-C-(hydroxymethyl)-D-glycerotetrose
apio-β-D-furanosylIdentifiers CAS number 639-97-4 PubChem 4658 ChemSpider 16735670 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O[C@]1(CO)COC(O)[C@@H]1O
Properties Molecular formula C5H10O5 Molar mass 150.13 g/mol Exact mass 150.052823  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Apiose is a branched-chain sugar found as residues in galacturonans-type pectins; that occurs in parsley and many other plants.
Apiose 1-reductase uses D-apiitol and NAD+ to produce D-apiose, NADH, and H+.
Flavone apiosyltransferase uses UDP-apiose and 5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavone 7-O-beta-D-glucoside to produce UDP, 5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavone (apigenin), and [[7-O-[beta-D-apiosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside]]].
External links
Categories:- Aldopentoses
- Biochemistry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
