- Tuition payments
-
"Tuition" redirects here. For Tutoring, see Tutor.For tuition fees in the United Kingdom, see Tuition fees in the United Kingdom.For college tuition in United States, see College tuition in United States.
Tuition payments, known primarily as tuition in American English[citation needed] and as tuition fees in British English, Canadian English, Australian English, New Zealand English and Indian English[citation needed], refers to a fee charged for educational instruction during higher education.
Tuition payments are charged by educational institutions in some countries to assist with funding of staff and faculty, course offerings, lab equipment, computer systems, libraries, facility upkeep and to provide a comfortable student learning experience.
Contents
Tuition payment
Some methods students use to pay for the cost of tuition include:
- Scholarships
- Bursaries
- Grants
- Parents' money
- Student savings
- Government Student loans
- Financial institution loans
- Educational institution loans
- Company funding
Tuition is one of the costs of a post-secondary education in the U.S. The total cost of college in the U.S. is called the cost of attendance or the "sticker price" and in addition to tuition it can include room and board, travel expenses, books, fees, and other expenses such as computers.
Most students (and their families) who pay for tuition and other education costs don't have enough savings to pay in full while they are in school.[citation needed] Some students must work and/or borrow money to afford an education. In the U.S., student financial aid is available to defray the cost of a post-secondary education.
Students have private tuition for any one of a number of reasons:
- To improve grades
- To get into a particular school, college or university
- To assist with Special Needs
- To undertake corporate training for their company
- General improvement (adult learners)
Developed countries have adopted a dual scheme for education: while basic (i.e. high-school) education is supported by taxes rather than tuition, higher education is usually given for a fee or tuition.
History of tuition payments
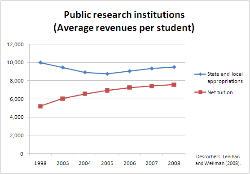 Study comparing college revenue per student by tuition and state funding in 2008 dollars.[1]
Study comparing college revenue per student by tuition and state funding in 2008 dollars.[1]
In medieval Europe, the universities were institutions of the Roman Catholic Church. As they mainly trained clergy, these universities did not have any need to exact fees from the students.[citation needed] Their situation was comparable with the modern corporate universities and military academies.
Later in most Protestant countries, the main duty of the universities was the training of future civil servants. Again, it was not in the interest of the state to charge tuition fees, as this would have decreased the quality of civil servants. On the other hand, the number of students from the lower classes was usually kept in check by the expenses of living during the years of study, although as early as the middle 19th century there were calls for limiting the university entrance by middle-class persons.[citation needed] However, a typical family could not afford educating a son, let alone a daughter, even if the education itself was free. A similar situation exists today in many Third World countries, where the expenses of "free" school (e.g., food, books, school uniform) prevent some children from attending even primary school.
After World War II, an enhanced standard of living and the existence of free university education in many countries enabled more working-class youths to receive a degree, resulting in the inflation of education and enlarged middle classes. In countries with tuition fees, similar progress was effected with state study loans, grants, scholarships, the G.I. Bill, and other financial instruments. It has been proposed[who?] that the strong class separations visible in British society result from the fact that the expansion of education there has been less efficient than in continental Europe.[citation needed]
See also
- College tuition in United States
- Tuition fees in the United Kingdom
- EdFund
- Free education
- Higher education bubble
- Higher Education Price Index
- Post-secondary education
- Private university
- Student benefit
- Student debt
- Student loan
- Student loans in the United States
- Tuition agency
- Tuition center
- Tuition freeze
References
- ^ "Trends in College Spending 1998-2008" Delta Cost Project.
- Cauchon, Dennis (June 27, 2004). "Grants more than offset soaring university tuition". Nation (USA Today). http://www.usatoday.com/news/nation/2004-06-27-demystifying-tuition_x.htm. Retrieved 2006-05-11.
Categories:- Education finance
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
