- Chaudière River
-
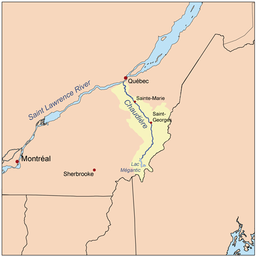
Chaudière River Chutes-de-la-ChaudièreCountry Canada State Quebec Source Lake Mégantic - location Lac-Mégantic, Estrie - coordinates 45°34′20″N 70°53′00″W / 45.57222°N 70.8833333°W Mouth Saint Lawrence River - location Lévis, Chaudière-Appalaches - coordinates 46°44′34″N 71°16′43″W / 46.74278°N 71.27861°W Length 185 km (115 mi) Basin 6,682 km2 (2,580 sq mi) Discharge - average 114 m3/s (4,030 cu ft/s) - max 470 m3/s (16,600 cu ft/s) - min 11 m3/s (390 cu ft/s) The Chaudière River (French for "Cauldron" or "Boiler River") is a 185 kilometres (115 mi) long river with its source near the Town of Lac-Mégantic, in southeast Quebec, Canada. From its source Lake Megantic in the Chaudière-Appalaches region, it runs northwards to flow into the St. Lawrence River opposite Quebec City. The river's drainage area is 6682 square kilometres, initially in the Appalachian Mountains, then in the low-lands of the St. Lawrence, and include 236 lakes covering 62 square kilometres and approximately 180,000 inhabitants. Its annual medium flow at the station of Saint-Lambert-de-Lauzon is 114 m³/s, varying from 11 m³/s (low water) to 470 m³/s (spring high water), with historical maximum of 1760 m³/s.
Its principal tributaries are:
- Rivière du Loup (not to be confused with Rivière du Loup in the Bas-Saint-Laurent), also known as the Rivière Linière
- Famine River
- Beaurivage River
- Saint-Victor River
The river's basin has nearly 50% of the faunal richness of Quebec, namely 330 out of 653 vertebrate species known in the province can be found here.
The river, and the 40 metres (130 ft) high Chaudière Falls which it passes over en route, are popular outdoor recreation areas.
Contents
History
The Abenaki indigenous people resided close to the Chaudière Falls and named it “Kikonteku”, meaning “River of the Fields”. On the charts of Samuel de Champlain, it was given the name “Etchemin River” (a name now used for another river whose drainage area borders with that of the Chaudière River). It was called "Rivière du Sault de la Chaudière" for a period of time before it became simply "Rivière Chaudière" towards the end of the 18th century. This name refers to the waterfall close to its mouth.
Its location was strategic for French colonization during the 18th century because the river was a natural link between New France and the British colonies to the south. It was also used by Benedict Arnold at the time of his 1775 expedition in the invasion of Quebec.
In 1823, gold was found along its shores in the Eastern Townships of Quebec.[1]
The river today
The Chaudière valley mostly crosses the Beauce area. The river impacts its industries and way of life, particularly during spring run-off, when it frequently overflows into populated areas, in spite of the 160 dams and levees. The river flows through several cities and villages of the area such as Sainte-Marie, Saint-Georges, Beauceville, and Saint-Joseph-de-Beauce.
The river is a popular location for outdoor sports, particularly at Lac-Mégantic and at Parc des Chutes-de-la-Chaudière 46°42′53.35″N 71°16′57.09″W / 46.7148194°N 71.282525°W. Located close to the mouth of the river at Lévis, this park offers cycling and hiking trails, as well as a footbridge suspended above the river which offers a view of the waterfalls.
The falls have been harnessed for hydro-electric power since the beginning of the 20th century. The dam was rebuilt in 1999 on the remains of the old installations, and now consists of a small 24 MW power station.
Notes
- ^ Law-West, Don. "Gold", in The Canadian Encyclopedia (Edmonton: Hurtig Publishing, 1988), Volume 2, p.908.
External links
Categories:- Rivers of Quebec
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.