- Odessa Meteor Crater
-
Odessa Meteor Crater National Natural Landmark MuseumCountry  United States
United StatesState  Texas
TexasRegion Ector County District Permian Basin Elevation 930 m (3,051 ft) Coordinates 31°45′22.02″N 102°28′44.06″W / 31.7561167°N 102.4789056°W Geology Meteor Crater Founded U.S. National Natural Landmark Date 1965 Management Ector County The Odessa Meteor Crater is a meteorite crater in the southwestern part of Ector County, southwest of the city of Odessa, Texas, United States. It is located approximately 3 miles (5 km) south of I-20 at FM 1936 south.[1] This is one of two impact crater sites found in Texas, the other being the much larger and older Sierra Madera crater.
The Handbook of Texas Online describes the Odessa meteor crater as the largest of several smaller craters in the immediate area that were formed by the impact of thousands of octahedrites (an iron metallic type) that fell in prehistoric times.[2]
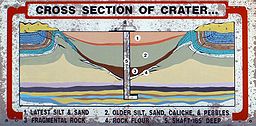
The web site of the University of Texas of the Permian Basin (UTPB, Center for Energy and Economic Diversification (CEED)), identifies five craters at the Odessa site and shows a distribution map of the meteorite fragments recovered from the area.[3] The recoveries have generally come from an area to the north and northwest of the main crater site, with only a few found to the south. They indicate that the structure of the main crater, because it was one of the earliest to be recognized and studied, is now used to name similar impact sites on a worldwide basis. Over 1500 meteorites have been recovered from the surrounding area over the years, the largest of which weighed approximately 300 pounds (135 kg), but excavations in the main crater confirm that there is no meteorite mass underground and probably never has been. The site has been designated as a National Natural Landmark by the National Park Service, and a small information area and nature trail has been set up on-site for a self-guided tour.
It is 168 meters (~550 feet) in diameter and the age is estimated to be around 63,500 years (Pleistocene or younger).[4] The crater is exposed to the surface, and was originally about 100 feet (30 meters) deep. Due to subsequent infilling by soil and debris, the crater is currently 15 feet (5 meters) deep at its lowest point, which provides enough relief to be visible over the surrounding plains, but does not offer the dramatic relief found at the more famous Meteor Crater in Arizona.
Still, the site offers an excellent opportunity to view a relatively uncommon impact feature close to a major transportation artery near a major city.
See also
- Impact crater
- List of impact craters in North America
- Marquez crater
References
- ^ "Odessa". Earth Impact Database. University of New Brunswick. http://www.passc.net/EarthImpactDatabase/odessa.html. Retrieved 2008-12-30.
- ^ Smith, Julia Cauble. "Meteor crater at Odessa". Handbook of Texas Online. http://www.tshaonline.org/handbook/online/articles/MM/rym1.html. Retrieved 5 November 2009.
- ^ Anonymous. "Meteor Impact Structures". Center for Energy & Economic Diversification, The University of Texas of the Permian Basin. http://ceed.utpb.edu/geology-resources/west-texas-geology/meteor-impact-structures/. Retrieved 5 November 2009.
- ^ Holliday, V.T., Kring, D.A., Mayer, J.H. and Goble, R.J. 2005. Age and effects of the Odessa meteorite impact, western Texas, USA. Geology 33(12):945-948.
External links
 Media related to Odessa Meteor Crater at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Odessa Meteor Crater at Wikimedia Commons- UTPB Center for Energy and Economic Diversifications, Odessa Meteor Craters
- Odessa Meteor Crater and Museum website
- Article about the crater
Categories:- Earth Impact Database
- Protected areas of Ector County, Texas
- Geography of Texas
- Geology museums in the United States
- Impact craters of the United States
- Museums in Ector County, Texas
- Natural history museums in Texas
- Pleistocene impact craters
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.