- Dental papilla
-
Dental papilla 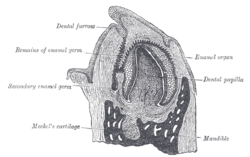
Vertical section of the mandible of an early human fetus. X 25. (Dental papilla labeled at center right.) 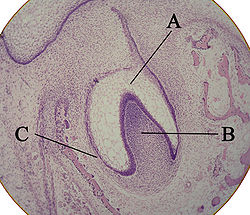
Histologic slide showing a tooth bud.
A: enamel organ
B: dental papilla
C: dental follicleLatin papilla dentis Gray's subject #242 1122 MeSH Dental+papilla Code TE E04.0.3.3.1.0.12 The dental papilla is a condensation of ectomesenchymal cells called odontoblasts, seen in histologic sections of a developing tooth. It lies below a cellular aggregation known as the enamel organ. The dental papilla appears after 8-10 weeks intra uteral life. The dental papilla gives rise to the dentin and pulp of a tooth.
The enamel organ, dental papilla, and dental follicle together forms one unit, called the tooth germ. This is of importance because all the tissues of a tooth and its supporting structures form from these distinct cellular aggregations.
See also
References
- Cate, A.R. Ten. Oral Histology: development, structure, and function. 5th ed. 1998. ISBN 0-8151-2952-1.
External links
- Dental+papilla at eMedicine Dictionary
Tooth development (TE 5.4) -blast General Dental papilla · Epithelial root sheath · Epithelial cell rests of Malassez
Enamel organ: Outer enamel epithelium · Inner enamel epithelium · Stellate reticulum · Stratum intermedium
Dentition · Teething · Tooth eruptionPulp occlusion Canalis amelodentineus · Fovea enamelea · Fovea dentinea - Parts of tooth
- Dentistry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
