- Kyanite
-
Kyanite 
General Category Silicate mineral Chemical formula Al2SiO5 Crystal symmetry Triclinic pinacoidal H–M Symbol: 1 Space group: P1 Unit cell a = 7.1262(12) Å,
b = 7.852(10) Å,
c = 5.5724(10) Å
α = 89.99(2)°, β = 101.11(2)°, γ = 106.03(1)°
Z = 4Identification Color Blue, white, rarely green, gray, yellow, pink, orange, and black, can be zoned Crystal habit Columnar; fibrous; bladed Crystal system Triclinic Twinning Lamellar on {100} Cleavage [100] perfect [010] imperfect with 79° angle between Fracture Splintery Tenacity Brittle Mohs scale hardness 4.5-5 parallel to one axis
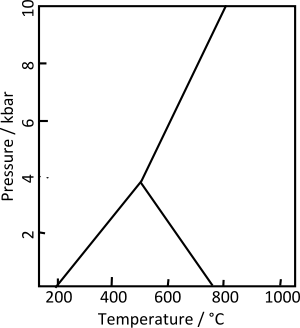
6.5-7 perpendicular to that axisLuster Vitreous to pearly Streak White Diaphaneity Transparent to translucent Specific gravity 3.53 - 3.65 measured; 3.67 calculated Optical properties Biaxial (-) Refractive index nα = 1.712 - 1.718 nβ = 1.720 - 1.725 nγ = 1.727 - 1.734 Pleochroism Trichroic, colorless to pale blue to blue 2V angle 78°-83° References [1][2][3] Kyanite, whose name derives from the Greek word kuanos sometimes referred to as "kyanos", meaning deep blue, is a typically blue silicate mineral, commonly found in aluminium-rich metamorphic pegmatites and/or sedimentary rock. Kyanite in metamorphic rocks generally indicates pressures higher than 4 kilobars. Although potentially stable at lower pressure and low temperature, the activity of water is usually high enough under such conditions that it is replaced by hydrous aluminosilicates such as muscovite, pyrophyllite, or kaolinite. Kyanite is also known as disthene, rhaeticite and cyanite.
Kyanite is a member of the aluminosilicate series, which also includes the polymorph andalusite and the polymorph sillimanite. Kyanite is strongly anisotropic, in that its hardness varies depending on its crystallographic direction. In Kyanite, this anisotropism can be considered an identifying characteristic.
At temperatures above 1100 °C kyanite decomposes into mullite and vitreous silica via the following reaction: 3(Al2O3·SiO2) → 3Al2O3·2SiO2 + SiO2. This transformation results in an expansion.[4]
Contents
Uses of kyanite
Kyanite is used primarily in refractory and ceramic products, including porcelain plumbing fixtures and dishware. It is also used in electronics, electrical insulators and abrasives.
Kyanite has been used as a semiprecious gemstone, which may display cat's eye chatoyancy, though this use is limited by its anisotropism and perfect cleavage. Color varieties include recently discovered orange kyanite from Tanzania.[citation needed] The orange color is due to inclusion of small amounts of manganese (Mn3+) in the structure.[5]
Kyanite is one of the index minerals that are used to estimate the temperature, depth, and pressure at which a rock undergoes metamorphism.
Notes for identification
Kyanite's elongated, columnar crystals are usually a good first indication of the mineral, as well as its color (when the specimen is blue). Associated minerals are useful as well, especially the presence of the polymorphs of staurolite, which occur frequently with kyanite. However, the most useful characteristic in identifying kyanite is its anisotropism. If one suspects a specimen to be kyanite, verifying that it has two distinctly different hardnesses on perpendicular axes is a key to identification.
Occurrence
Kyanite occurs in gneiss, schist, pegmatite, and quartz veins resulting from moderate to high-pressure regional metamorphism of principally pelitic rocks. It occurs as detrital grains in sedimentary rocks. It occurs associated with staurolite, andalusite, sillimanite, talc, hornblende, gedrite, mullite and corundum.[1]
References
- ^ a b Handbook of Mineralogy
- ^ MinDat
- ^ Webmineral data
- ^ Speyer, Robert (1993). Thermal Analysis of Materials. CRC Press. pp. 166. ISBN 0824789636. http://books.google.com/?id=5vTPIN_Y_FMC&printsec=frontcover#PPA166,M1.
- ^ M. Gaft, et.al., Laser-induced time-resolved luminescence of orange kyanite Al2SiO5, (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925346711002138)
- ^ Whitney, D.L. (2002), "Coexisting andalusite, kyanite, and sillimanite: Sequential formation of three Al2SiO5 polymorphs during progressive metamorphism near the triple point, Sivrihisar, Turkey", American Mineralogist 87 (4): 405–416, http://ammin.geoscienceworld.org/cgi/content/abstract/87/4/405
- Mineral Galleries
- Faye, G. H.; Nickel, E. H. (1969). "On the origin of colour and pleochroism of kyanite". The Canadian Mineralogist 10: 35–46. http://rruff.info/rruff_1.0/uploads/CM10_35.pdf.
Categories:- Gemstones
- Aluminium minerals
- Nesosilicates
- Triclinic minerals
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.