Minimum resolvable contrast
- Minimum resolvable contrast
-
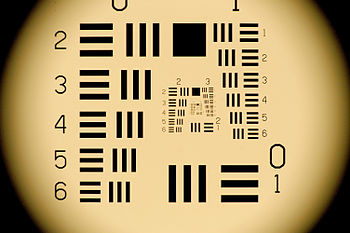
The 1951 USAF Tri-bar Resolution Test Target is a classic example of a three bar target for the
MRC test. The target is typically illuminated by an
integrating sphere irradiating in the visible spectrum.
Minimum resolvable contrast (MRC) is a subjective measure of a visible spectrum sensor’s or camera's sensitivity and ability to resolve data. A snapshot image of a series of three bar targets of selected spatial frequencies and various contrast coatings captured by the UUT (Unit Under Test) are used to determine the MRC of the UUT, i.e the visible spectrum camera or sensor. A trained observer selects the smallest target resolvable at each contrast level. Typically, specialized computer software collects the inputed data of the observer and provides a graph of contrast v.s. spatial frequency at a given luminance level. A first order polynomial is fitted to the data and an MRC curve of spatial frequency versus contrast is generated.[1]
See also
References
- ^ Electro Optical Industries, Inc. (2005) EO TestLab Methodology. In Education/Ref. http://www.electro-optical.com/html/toplevel/educationref.asp
External links
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Minimum resolvable temperature difference — (MRTD) is a measure for assessing the performance of infrared cameras, and is inversely proportional to the modulation transfer function. Typically, an operator is asked to assess the minimum temperature difference at which a 4 bar target can be… … Wikipedia
Modulation transfer function (infrared imaging) — The Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) is used to approximate the position of best focus of an infrared imaging system. In an imaging system, best focus is typically achieved when the MTF is between 0.4 and 0.6; most often at 0.5 (50% cutoff… … Wikipedia
Optical resolution — This article is about optical resolution in optics. For the method of separating enantiomers in chemistry, see Chiral resolution. Optical resolution describes the ability of an imaging system to resolve detail in the object that is being imaged.… … Wikipedia
Signal transfer function — The signal transfer function (SiTF) is a measure of the signal output versus the signal input of a system such as an infrared system or sensor. [cite book | title = The Optical Transfer Function of Imaging Systems | author = Tom L. Williams |… … Wikipedia
Signal to noise ratio (image processing) — The Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) is used in image processing as a physical measure of the sensitivity of an imaging system. Industry standards measure SNR in decibels (dB) and therefore apply the 20 log rule to the pure SNR ratio. In turn,… … Wikipedia
Image resolution — describes the detail an image holds. The term applies equally to digital images, film images, and other types of images. Higher resolution means more image detail. Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Basically, resolution quantifies … Wikipedia
Distortion — This article is about technology, especially electrical engineering. For other uses, see Distortion (disambiguation). Distort redirects here. For other uses, see Distort (disambiguation). A distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or… … Wikipedia
MRC — may refer to: in government, Medical Reserve Corps, US network of community based units sponsored by the Office of the Surgeon General Municipalité régionale de comté (or regional county municipality), a type of territorial division and… … Wikipedia
MRC — ist die Abkürzung für: Management Risk Controlling, eine zentrale Unternehmensaufgabe, die sich insbesondere auf die Unterstützung organisatorischer Sicherungsmaßnahmen, Verbesserung der internen Revision sowie die Dokumentation und Einhaltung… … Deutsch Wikipedia
eye, human — ▪ anatomy Introduction specialized sense organ capable of receiving visual images, which are then carried to the brain. Anatomy of the visual apparatus Structures auxiliary to the eye The orbit The eye is protected from mechanical injury… … Universalium


