Cation-anion radius ratio
- Cation-anion radius ratio
-
In condensed matter physics the cation-anion radius ratio is the ratio of the ionic radius of the cation to the ionic radius of the anion in a cation-anion compound. This is simply given by rC / rA
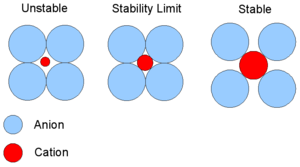
The allowed size of the cation is determined by the critical radius ratio. If the cation is too small, then it will attract the anions into each other and they will collide hence the compound would collapse, this occurs when the radius ratio drops below 0.155.
At the stability limit the cation is touching all the anions and the anions are just touching at their edges (radius ratio = 0.155). Beyond this stability limit (radius ratio > 0.155) the compound will be stable.
The below table gives the relation between radius ratio and coordination number
| Radius Ratio |
Coordination number |
Type of void |
Example |
| 0.155-0.225 |
3 |
Triangular Planar |
B2CO3 |
| 0.225-0.414 |
4 |
Tetrahedral |
ZnS,CuCl |
| 0.414-0.732 |
6 |
Octahedral |
NaCl,MgO |
| 0.732-1.000 |
8 |
Cubic |
CsCl,NH4Br |
Face-centered_cubic
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Cubic crystal system — A rock containing three crystals of pyrite (FeS2). The crystal structure of pyrite is simple cubic, and this is reflected in the cubic symmetry of its natural crystal facets … Wikipedia
Metal ions in aqueous solution — A metal ion in aqueous solution is a cation, dissolved in water, of chemical formula [M(H2O)n]z+. The solvation number, n, determined by a variety of experimental methods is 4 for Li+ and Be2+ and 6 for elements in rows 3 and 4 of the periodic… … Wikipedia
Pauling's rules — are five rules published by Linus Pauling in 1929 [cite journal last= |first= |authorlink= Pauling L |coauthors= |year= 1929|month= |title= The principles determining the structure of complex ionic crystals |journal= J. Am. Chem. Soc.|volume= 51… … Wikipedia
Rubidium chloride — Chembox new Name = Rubidium chloride ImageFile = Rubidium chloride 3D ionic.png ImageName = Rubidium chloride s NaCl structure ImageFile1 = Rubidium chloride CsCl structure 3D ionic.png ImageName1 = Rubidium chloride s CsCl structure OtherNames … Wikipedia
chemical compound — Introduction any substance composed of identical molecules consisting of atoms (atom) of two or more chemical elements (chemical element). All the matter in the universe is composed of the atoms of more than 100 different chemical elements … Universalium
chemical bonding — ▪ chemistry Introduction any of the interactions that account for the association of atoms into molecules, ions, crystals, and other stable species that make up the familiar substances of the everyday world. When atoms approach one another … Universalium
Hydrogen — This article is about the chemistry of hydrogen. For the physics of atomic hydrogen, see Hydrogen atom. For other meanings, see Hydrogen (disambiguation). ← hydrogen → helium … Wikipedia
mass spectrometry — or mass spectroscopy Analytic technique by which chemical substances are identified by sorting gaseous ions by mass using electric and magnetic fields. A mass spectrometer uses electrical means to detect the sorted ions, while a mass spectrograph … Universalium
Nanofluidic circuitry — is a nanotechnology aiming for control of fluids in nanometer scale. Due to the effect of an electrical double layer within the fluid channel, the behavior of nanofluid is observed to be significantly different compared with its microfluidic… … Wikipedia
Gold — This article is about the metal. For the color, see Gold (color). For other uses, see Gold (disambiguation). platinum ← gold → mercury … Wikipedia