- Deflection (physics)
-
In physics deflection is the event where an object collides and bounces against a plane surface.
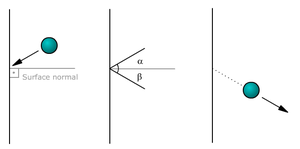
In such collisions involving a sphere and a plane, the collision angle formed with the surface normal (the incidental angle α) must equal the bounce angle (the accidental angle β), α = β.[citation needed]
Magnetic deflection refers to Lorentz forces acting upon a charged particle moving in a magnetic field.
An object's deflective efficiency can never equal or surpass 100%. For example, a mirror will never reflect exactly the same amount of light cast upon it. Also, a ball in free-fall (meaning no forces are acting on it other than gravity), upon hitting the ground, will never bounce back up to the spot where it first started to descend. This is due to the Laws of Thermodynamics, which state that, in every action, some energy being used in that action escapes into the environment.
See also
Categories:- Fundamental physics concepts
- Physics stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.