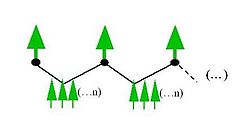
- Double-pair mating
-
Double-pair mating (DPM) is a mating (crossing) design used in plant breeding. Each individual is mated with two others.
Principles
In Fig. 1 a connected variant of DPM is shown. DPM is an efficient mating design in balanced breeding programmes, where equal contribution from each breeding population member is desired.[1] With DPM the number of new families created is equal to the number of individuals mated. DPM allows to efficiently utilise positive assortative mating for more efficient use of the breeding population members for deployment to seed orchards.[2] In comparison with single pair mating, DPM has the advantages that the genes from the individual are transmitted to next generation even if one of the crosses fails; that safer estimates of breeding values of the parents get possible (useful for seed orchards, where tested trees are preferred); and that genes from different ancestors have a better chance to combine.
References
- ^ Rosvall, O. 1999. Enhancing Gain from Long-Term Forest Tree Breeding while Conserving Genetic Diversity. PhD-thesis. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae Sueciae. Silvestria 109 65pp+4 chapters
- ^ Ruotsalainen, S. 2002. Managing breeding stock in the initiation of a long-term tree breeding program. PhD-thesis. Finnish Forest Research Institute, Research Papers 875., 95 + 61 p[1]
Categories:- Genetics
- Forestry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.