- OBSL1
-
Obscurin-like 1 
PDB rendering based on 2cpc.Available structures PDB 2CPC, 2E6P, 2E6Q, 2WP3, 2WWK, 2WWM, 3KNB Identifiers Symbols OBSL1; KIAA0657; MGC71026 External IDs OMIM: 610991 HomoloGene: 28013 GeneCards: OBSL1 Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • cytoskeletal adaptor activity Cellular component • intercalated disc
• Z disc
• M band
• perinuclear region of cytoplasmBiological process • cytoskeleton organization
• cardiac myofibril assemblySources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 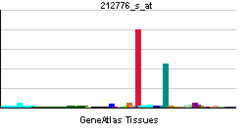
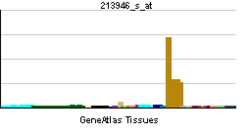
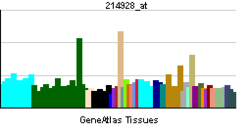
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 23363 n/a Ensembl ENSG00000124006 n/a UniProt O75147 n/a RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001173408.1 n/a RefSeq (protein) NP_001166879.1 n/a Location (UCSC) Chr 2:
220.42 – 220.44 Mbn/a PubMed search [1] n/a Obscurin-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OBSL1 gene.[1][2]
References
- ^ Ishikawa K, Nagase T, Suyama M, Miyajima N, Tanaka A, Kotani H, Nomura N, Ohara O (Dec 1998). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. X. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which can code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res 5 (3): 169–76. doi:10.1093/dnares/5.3.169. PMID 9734811.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: OBSL1 obscurin-like 1". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=23363.
Further reading
- Nakajima D, Okazaki N, Yamakawa H, et al. (2003). "Construction of expression-ready cDNA clones for KIAA genes: manual curation of 330 KIAA cDNA clones.". DNA Res. 9 (3): 99–106. doi:10.1093/dnares/9.3.99. PMID 12168954.
- Geisler SB, Robinson D, Hauringa M, et al. (2007). "Obscurin-like 1, OBSL1, is a novel cytoskeletal protein related to obscurin.". Genomics 89 (4): 521–31. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2006.12.004. PMC 1885211. PMID 17289344. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1885211.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs.". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Yu W, Andersson B, Worley KC, et al. (1997). "Large-scale concatenation cDNA sequencing.". Genome Res. 7 (4): 353–8. doi:10.1101/gr.7.4.353. PMC 139146. PMID 9110174. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139146.
- Andersson B, Wentland MA, Ricafrente JY, et al. (1996). "A "double adaptor" method for improved shotgun library construction.". Anal. Biochem. 236 (1): 107–13. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0138. PMID 8619474.
External Links
PDB gallery Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 2 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.