- DDX52
-
DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 52 Identifiers Symbols DDX52; HUSSY19; ROK1 External IDs OMIM: 612500 MGI: 1925644 HomoloGene: 5093 GeneCards: DDX52 Gene EC number 3.6.4.13 Gene Ontology Molecular function • nucleotide binding
• RNA binding
• helicase activity
• ATP binding
• ATP-dependent helicase activity
• hydrolase activityCellular component • nucleus
• nucleolusSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 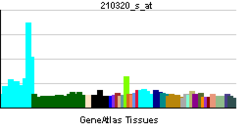
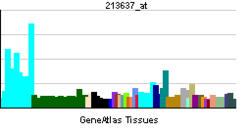
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 11056 78394 Ensembl ENSG00000141141 ENSMUSG00000020677 UniProt Q9Y2R4 Q3TKX4 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_007010.3 NM_030096.2 RefSeq (protein) NP_008941.2 NP_084372.2 Location (UCSC) Chr 17:
35.97 – 36 MbChr 11:
83.76 – 83.78 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX52 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DDX52 gene.[1][2]
References
- ^ Stanchi F, Bertocco E, Toppo S, Dioguardi R, Simionati B, Cannata N, Zimbello R, Lanfranchi G, Valle G (Jan 2001). "Characterization of 16 novel human genes showing high similarity to yeast sequences". Yeast 18 (1): 69–80. doi:10.1002/1097-0061(200101)18:1<69::AID-YEA647>3.0.CO;2-H. PMID 11124703.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: DDX52 DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 52". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=11056.
Further reading
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes.". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1356129.
- Andersen JS, Lam YW, Leung AK, et al. (2005). "Nucleolar proteome dynamics.". Nature 433 (7021): 77–83. doi:10.1038/nature03207. PMID 15635413.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs.". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Scherl A, Couté Y, Déon C, et al. (2003). "Functional proteomic analysis of human nucleolus.". Mol. Biol. Cell 13 (11): 4100–9. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-05-0271. PMC 133617. PMID 12429849. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=133617.
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, et al. (2002). "Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus.". Curr. Biol. 12 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00650-9. PMID 11790298.
Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 17 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
