- Oriental cockroach
-
Oriental cockroach 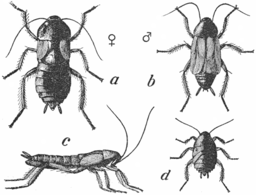
A: Female
B: Male
C: Side view of female
D: Young maleScientific classification Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Insecta Order: Blattodea Family: Blattidae Genus: Blatta Species: B. orientalis Binomial name Blatta orientalis
Linnaeus, 1758The oriental cockroach (also known as: waterbug and Blatta orientalis) is a large species of cockroach, measuring about 1 in (2.5 cm) in length at maturity. It is dark brown to black in colour and has a glossy body. The female Oriental cockroach has a somewhat different appearance to the male, appearing to be wingless at casual glance but has two very short and useless wings just below her head. She has a wider body than the male. The male has long wings, which cover a majority of his body and are brown in colour, and has a more narrow body. The odd male is capable of very short flights, ranging about 2 to 3 meters. The female oriental cockroach looks somewhat similar to the Florida woods cockroach, and may be mistaken for it.
Habitat
The oriental cockroach tends to travel somewhat more slowly than other species. They are often called "waterbugs" since they prefer dark, moist places. They can often be found around decaying organic matter, and in sewers, drains, damp basements, porches, and other damp locations. They can be found outside in bushes, under leaf groundcover, under mulch, and around other damp places outdoors. It is a major household pest in parts of the northwest, mid-west, and southern United States[1].
Adaptation
In order to thrive, cockroaches need a place to hide. They prefer warm places and a relatively high humidity if possible; they also need a source of food/liquid. The optimum temperature for oriental cockroaches is between 20 °C (68 °F) to 29 °C (84 °F). Female oriental cockroaches have vestigial tegmina (reduced forewings) and males have longer tegmina. Cockroaches are mainly nocturnal. Oriental cockroaches can be elusive in that a casual inspection of an infested dwelling during the day may show no signs of roach activity.
Distinction
Signs of cockroaches are their oothecae, which are “egg cases” containing up to 16 individual eggs in the case of oriental cockroaches. These oothecae are dropped by females and hatch on their own in about two months. Oriental cockroaches can be harder to get rid of than other roaches. Although adults can be fairly easily killed by the application of residual insecticide, the insecticides can get washed away, and two months later females can hatch new nymphs.
Comparison of three common roaches
Roach German cockroach Oriental cockroach American cockroach Size 12 mm (1.2 cm) to 15 mm (1.5 cm) 25 mm (2.5 cm) to 30 mm (3.0 cm) 28 mm (2.8 cm) to 43 mm (4.3 cm) Habitat Heated buildings, optimum 32 °C (90 °F) 20 °C (68 °F) to 29 °C (84 °F) Same as German Nymphal development time 6 to 12 weeks 6 to 12 months 4 to 15 months Life Span 6 to 9 months 1 to 1.5 years 1 to 1.5 years Able to fly? No No Yes Image gallery
-
Blatta orientalis in the process of molting.
References
External links
- oriental cockroach on the UF / IFAS Featured Creatures Web site
- oriental cockroach egg parasitoid on the UF / IFAS Featured Creatures Web site.
Categories:- Cockroaches
- Household pest insects
- Animals described in 1758
- Urban animals
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.





