- Angular mil
-
An angular mil, also mil, is a unit of angle. All versions of the angular mil are approximately the same size as a trigonometric milliradian.
Contents
History
The milliradian was first identified in the mid nineteenth Century. Degrees and minutes were the usual units of angular measurement but others were being proposed, with 'grads' (circle/400) under various names having considerable popularity in much of northern Europe, the grad was based on dividing a right angle into 100 units. However, Imperial Russia used a different approach, dividing a circle into equilateral triangles and hence 600 units to a circle.
Around the time of the start of World War I, France was experimenting with the use of milliemes (circle/6400) for use with artillery sights instead of decigrades (circle/4000). The United Kingdom was also trialling them to replace degrees and minutes. They were adopted by France although decigrades also remained in use throughout World War I. Other nations also used decigrades. The United States, which copied many French artillery practices, adopted mils (circle/6400). After the Bolshevik Revolution and the adoption of the metric system of measurement (e.g. artillery replaced 'units of base' with metres) the Red Army expanded the 600 unit circle into a 6000 mil one, hence the Russian mil has nothing to do with milliradians as its origin.
In the 1950s, NATO adopted metric units of measurement for land and general use. Mils, metres and kilograms became standard, although degrees remained in use for naval and air purposes, reflecting civil practices.
Mathematical principle
Since a radian is mathematically defined as the angle formed when the length of a circular arc equals the radius of the circle, a trigonometric milliradian (mrad), is the angle formed when the length of a circular arc equals 1/1000 of the radius of the circle. Since the radian expresses a ratio, it is independent of the units of length used.
Use
The angular mil is commonly used by military organizations. Its relationship to the trigonometric radian gives rise to the handy property of subtension - that "One mil approximately subtends one metre at a distance of one thousand metres". More formally the small angle approximation for skinny triangles shows that the angle in radians approximates to the sine of the angle. More usefully an angular mil or mil subtends about 1 m at a range of 1,000 m.
Angle can be used for both calculating size or range. Where the range is known the angle will give the size, where the size is known then the range is given.
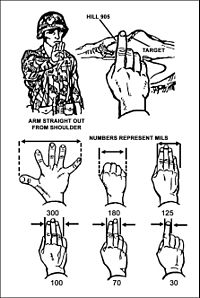
When out in the field angle can be measured by using calibrated optics or quite approximately ones fingers & hands. With an outstretched arm one finger is approximately 30 mils wide, a fist 150 mils and a spread hand 300 mils.
Angle can be used for calculating range. For objects of known size the range is the size divided by the angle. Land Rovers are about 3 to 4 m long, "smaller tank" or APC/MICV at ~6 m (e.g. T-34 or BMP) and ~10 m for a "big tank." From the front a Land Rover is about 1.5 m, most tanks around 3 - 3.5 m. So a SWB Land Rover from the side are one finger wide at ~100 m. A modern tank would have to be at a bit over 300 m.
Artillery spotters typically use their calibrated binoculars to walk fire onto a target. Here they know the approximate range to the target and so can read off the angle (+ quick calculation) to give the left/right corrections in metres.
Note: Do not confuse the angular mil with the MOA (minute of angle). 1 mil = 3.438 MOA
Markings on gunsights
Artillery sights
Artillery uses angular measurement in gun laying, the azimuth between the gun and its target many kilometres away and the elevation angle of the barrel. This means that artillery uses mils to graduate indirect fire azimuth sights (called dial sights or panoramic telescopes), their associated instruments (directors or aiming circles), their elevation sights (clinometers or quadrants), together with their manual plotting devices, firing tables and fire control computers.
Telescopic sights
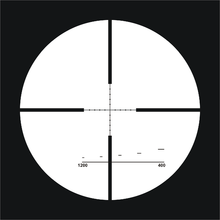 "FinDot" reticle as used by Finnish Defence Forces snipers (a regular Mil-dot reticle with the addition of 400 m – 1200 m holdover (stadiametric) rangefinding brackets for 1 meter high or 0.5 meter wide targets at 400, 600, 800, 1000 and 1200 m).
"FinDot" reticle as used by Finnish Defence Forces snipers (a regular Mil-dot reticle with the addition of 400 m – 1200 m holdover (stadiametric) rangefinding brackets for 1 meter high or 0.5 meter wide targets at 400, 600, 800, 1000 and 1200 m).
Many telescopic sights used on rifles have reticles that are marked in angular mils, and these are generally called Mil-dot scopes. The Mil-dots serve two purposes, range estimation and trajectory correction.
With a Mil-dot reticle-equipped scope the distance to an object can be estimated with a fair degree of accuracy by a trained user by determining how many angular mils an object of known size subtends. Once the distance is known, the drop of the bullet at that range (see external ballistics), converted back into angular mils, can be used to adjust the aiming point. Generally Mil-dot scopes have both horizontal and vertical crosshairs marked; the horizontal and vertical marks are used for range estimation and the vertical marks for bullet drop compensation. Trained users, however, can also use the horizontal dots to compensate for bullet drift due to wind. Mil-dot reticle-equipped scopes are most suited for long shots under uncertain conditions, such as those encountered by military and law enforcement snipers, varmint hunters and other field shooters. These riflemen must be able to aim at varying targets at unknown (sometimes long) distances, so accurate compensation for bullet drop is required.
Metric Mil-dot formula
Users who use the metric system are better off with a Mil-dot reticle, since they do not have to hassle with the unnecessary complications of a non metric system of measurement during mental calculations. Also the Mil-dot measurements and ranging calculations are always exact in the metric system.
To determine the distance or range to a target of known size at an unknown distance this formula can be applied:
where:
- D = distance or range to the target in meters
- S = size of the target in centimeters (known width or height of the target)
- mil = number of Mil-dots
To determine the size of a target at a known distance or range this formula can be applied:
Imperial and US customary units Mil-dot formula
To determine the distance to a target of known size: (Distance in yards) = 1000 / 36 x (Object size in inches) / Mils
To determine the size of a target at a known distance: (Object size in inches) = 36 / 1000 x (Distance in yards) x Mils
Knowing these relationships, you can set up a target range by drawing a vertical or horizontal line onto our target that is 3.6 inches long then backing up until the line is exactly one mil long in your scope for a 100 yard range, 7.2 inches for 200 yards, 10.8 inches for 300 yards, etc.
Known Target Size (8 inch) Ranging:
Target, inches Mils Distance, yards 8 0.1 2222 8 0.2 1111 8 0.3 741 8 0.4 556 8 0.5 444 8 0.6 370 8 0.7 317 8 0.8 278 8 0.9 247 8 1.0 222 8 1.1 202 8 1.2 185 8 1.3 171 8 1.4 159 8 1.5 148 8 2.0 111 8 2.2 101 8 3.0 74 8 4.0 56 8 5.0 44 8 6.0 37 8 7.0 32 8 8.0 28 8 9.0 25 8 10.0 22 Definitions of the angular mil
There are 2000π milliradians (≈ 6283.185 mrad) in a circle. So a milliradian is just under 1⁄6283 of a circle, or ≈ 3.438 minutes of arc. Each of the definitions of the angular mil are similar to that value but are easier to divide into many parts.
- 1⁄6400 of a circle in NATO countries.
- 1⁄6283 The “real” trigonometric unit of angular measurement of a circle in use by telescopic sight manufacturers using (stadiametric) rangefinding in reticles.
- 1⁄6000 of a circle in the former Soviet Union and Finland (Finland phasing out the standard in favour of the NATO standard).
- 1⁄6300 of a circle in Sweden. The Swedish term for this is streck, literally "line". Sweden has not been part of NATO nor the Warsaw Pact. Note however that Sweden is changing its map grid systems and angular measurement to those used by NATO, so the "streck" measurement is about to become obsolete.
See also
- mil (length)
- circular mil
External links
Categories:- Units of angle
- Decimalisation
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.