- Battle of Champion Hill
Infobox Military Conflict
conflict=Battle of Champion Hill
caption="Battle of Champion Hill"
sketched byTheodore R. Davis
partof=theAmerican Civil War
date=May 16 ,1863
place=Hinds County, Mississippi
result=Union victory
combatant1= flagicon|USA|1861United States (Union)
combatant2= flagicon|CSA|1863 CSA (Confederacy)
commander1=Ulysses S. Grant
commander2=John C. Pemberton
strength1=32,000Kennedy, pp. 167-70.]
strength2=22,000
casualties1=2,457 (410 killed, 1,844 wounded, 187 missing)
casualties2=3,840 (381 killed, 1,018 wounded, 2,441 missing/captured)The Battle of Champion Hill, or Bakers Creek, fought
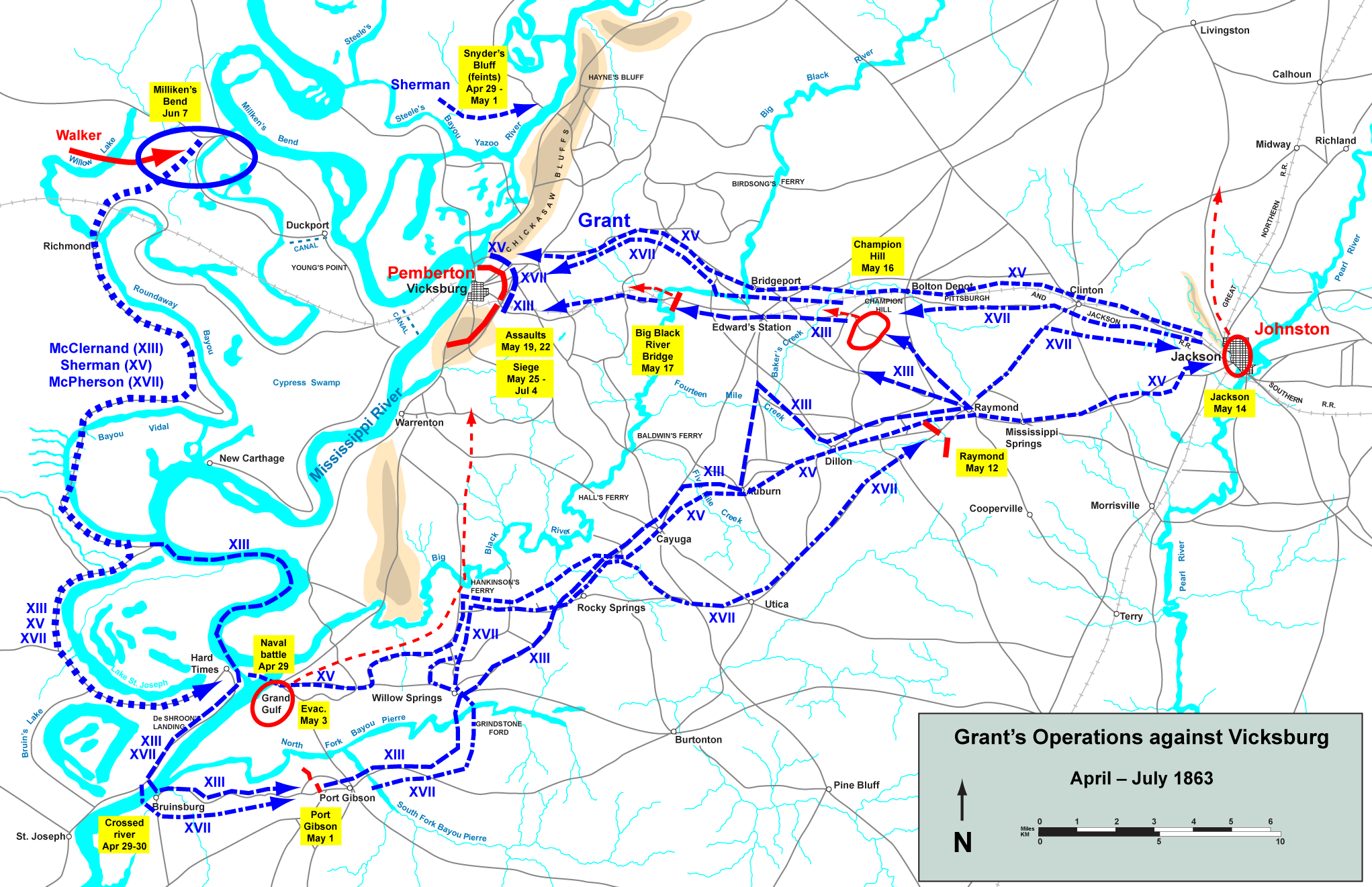
May 16 ,1863 , was the pivotal battle in theVicksburg Campaign of theAmerican Civil War . Union commanderMajor General Ulysses S. Grant and theArmy of the Tennessee pursued the retreating ConfederateLieutenant General John C. Pemberton and defeated his army twenty miles to the east ofVicksburg, Mississippi , leading inevitably to the Siege of Vicksburg and surrender.Background
Following the Union occupation of
Jackson, Mississippi , onMay 14 , both Confederate and Federal forces made plans for future operations. GeneralJoseph E. Johnston , commanding all Confederate forces inMississippi , retreated, with most of his army, up the Canton Road, but he ordered Lt. Gen. John C. Pemberton, commanding three divisions (about 23,000 men), to leave Edwards Station and attack the Federals at Clinton. Pemberton and his generals felt that Johnston’s plan was dangerous and decided instead to attack the Union supply trains moving from Grand Gulf to Raymond. On May 16, however, Pemberton received another order from Johnston repeating his former directions. Pemberton had already started after the supply trains and was on the Raymond-Edwards Road with his rear at the crossroads one-third mile south of the crest of Champion Hill. Thus, when he ordered a countermarch, his rear, including his many supply wagons, became the advance of his force.Battle
On
May 16 , at about 7:00 a.m., the Union forces engaged the Confederates and the Battle of Champion Hill began. Pemberton's force drew up into a three mile-long defensive line that ran from southwest to northeast along a crest of a ridge overlooking Jackson Creek. Grant observed in his "Personal Memoirs", "... where Pemberton had chosen his position to receive us, whether taken by accident or design, was well selected. It is one of the highest points in that section, and commanded all the ground in the range."Pemberton was unaware that one of the three Union columns was moving along the Jackson Road against his unprotected left flank on Champion Hill. For protection, Pemberton posted Brig. Gen.
Stephen D. Lee 'sAlabama brigade atop Champion Hill where they could watch for the reported Union column moving to the crossroads. Lee spotted the Union troops and they soon saw him. If this force was not stopped, it would cut the Rebels off from their Vicksburg base. Pemberton received warning of the Union movement and sent troops to his left flank. Union forces at the Champion House moved into action and emplaced artillery to begin firing.When Grant arrived at Champion Hill around 10:00 a.m., he ordered the attack to begin.
John A. McClernand 's corps attacked on the left,James B. McPherson 's on the right;William T. Sherman 's corps was well behind the others, departing Jackson. By 11:30 a.m., Union forces had reached the Confederate main line and at about 1:00 p.m., they took the crest while the troops fromCarter L. Stevenson 's division retired in disorder. McPherson's corps swept forward, capturing the crossroads and closing the Jackson Road escape route. The division ofJohn S. Bowen then counterattacked in support of Stevenson, pushing the Federals back beyond the Champion Hill crest before their surge came to a halt. They had insufficient troops to hold that position, however. Pemberton directedWilliam W. Loring to send forces from the southern area of the line (where they were only lightly engaged with McClernand's ineffective attack) to reinforce the Hill, but Loring refused, citing a strong Union presence to his front.
thumb|300px|Grant's Operations against Vicksburg.Grant then counterattacked, committing forces that had just arrived from Clinton by way of Bolton. Pemberton’s men could not stand up to this assault, so he ordered his men from the field to the one escape route still open: the Raymond Road crossing of Bakers Creek. By now, Loring had acceded to Pemberton's direction and marched toward the fighting, but by a circuitous route that kept them out of action. Brig. Gen.
Lloyd Tilghman 's brigade formed the rearguard, and they held at all costs, including the loss of Tilghman, a victim of artillery fire. In the late afternoon, Union troops seized the Bakers Creek Bridge, and by midnight, they occupied Edwards. The Confederates fell back to a defensive position at theBig Black River in front of Vicksburg. TheBattle of Big Black River Bridge there the next day would be the final chance for Pemberton to escape.Aftermath
Champion Hill was a bloody, but decisive, Union victory. In his "Personal Memoirs," Grant observed, "While a battle is raging, one can see his enemy mowed down by the thousand, or the ten thousand, with great composure; but after the battle these scenes are distressing, and one is naturally disposed to alleviate the sufferings of an enemy as a friend."
Grant criticized the lack of fighting spirit of his rival, McClernand, dissatisfied that he had not killed or captured Pemberton's entire force. McClernand's casualties were low on the Union left flank (south); McPherson's on the right were the bulk of the Union losses, about 2,500. The Confederates had about 3,800 casualties. Their effective loss included most of Loring's division, which had marched off to join
Joseph E. Johnston in Jackson.Battlefield preservation
Discontiguous portions of the battlefield, totaling over 800 acres (3.2 km²), are owned by the State of Mississippi. These properties are being held for possible future inclusion in
Vicksburg National Military Park . The Coker House stands adjacent to a south portion of the Champion Hill battlefield. It was used as a hospital by Federal forces and upon departing, they extensively looted both the house and the plantation stores. Bullet holes in the front door and jamb and cannonball holes on the west side of the Coker House remain as evidence of the Battle of Champion Hill. In 1985, the historic property was donated to the Jackson Civil War Roundtable and later deeded to the Mississippi Department of Archives and History. Presently the house is in ruins and its future history on the Champion Hill battlefield is unknown. Thousands of acres of the core battlefield are privately owned, listed as II.1. Class A (opportunity for comprehensive preservation, good integrity, low threat) by the Civil War Sites Advisory Commission.References
* [http://www.cr.nps.gov/hps/abpp/battles/ms009.htm National Park Service battle description]
* Grant, Ulysses S., [http://www.gutenberg.net/etext/4367 "Personal Memoirs of U. S. Grant"] , Charles L. Webster & Company, 1885–86, ISBN 0-914427-67-9.
* Kennedy, Frances H., ed., "The Civil War Battlefield Guide", 2nd ed., Houghton Mifflin Co., 1998, ISBN 0-395-74012-6.Notes
External links
* [http://battleofchampionhill.org Official Website of Champion Hill]
* [http://www.nps.gov/vick/vcmpgn/key.htm National Park Service, Vicksburg]
* [http://www.military.com/Resources/pics/civilwar_map21_largerview.jpg"West Point Atlas" map of Grant's advance from Jackson to Vicksburg]
* [http://www.cr.nps.gov/hps/abpp/cwsac/cwstab7.html Civil War Battlefields Listed by Preservation Priorities]
* [http://www.historyanimated.com/Vicksburg.html Animated History of The Battle for Vicksburg including Champion Hill]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.