- DDX39
-
DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 39A 
PDB rendering based on 1t5i.Available structures PDB 1t5i, 1t6n, 1xti, 1xtj, 1xtk Identifiers Symbols DDX39A; BAT1; BAT1L; DDX39; DDXL; MGC18203; MGC8417; URH49 External IDs MGI: 1915528 HomoloGene: 68487 GeneCards: DDX39A Gene EC number 3.6.4.13 Gene Ontology Molecular function • nucleotide binding
• nucleic acid binding
• helicase activity
• protein binding
• ATP binding
• ATP-dependent helicase activity
• hydrolase activityCellular component • nucleus Biological process • nuclear mRNA splicing, via spliceosome
• mRNA export from nucleus
• RNA splicingSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 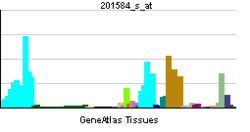
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 10212 68278 Ensembl ENSG00000123136 ENSMUSG00000005481 UniProt O00148 Q3T9L0 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_005804.3 NM_197982.3 RefSeq (protein) NP_005795 NP_932099.2 Location (UCSC) Chr 19:
14.52 – 14.53 MbChr 8:
86.24 – 86.25 MbPubMed search [1] [2] ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX39 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DDX39 gene.[1][2]
This gene encodes a member of the DEAD box protein family. These proteins are characterized by the conserved motif Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD) and are putative RNA helicases. They are implicated in a number of cellular processes involving alteration of RNA secondary structure, such as translation initiation, nuclear and mitochondrial splicing, and ribosome and spliceosome assembly. Based on their distribution patterns, some members of the DEAD box protein family are believed to be involved in embryogenesis, spermatogenesis, and cellular growth and division.[2]
References
- ^ Peelman LJ, Chardon P, Nunes M, Renard C, Geffrotin C, Vaiman M, Van Zeveren A, Coppieters W, van de Weghe A, Bouquet Y, et al. (Aug 1995). "The BAT1 gene in the MHC encodes an evolutionarily conserved putative nuclear RNA helicase of the DEAD family". Genomics 26 (2): 210–8. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(95)80203-X. PMID 7601445.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: DDX39 DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 39". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=10212.
Further reading
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, et al. (2002). "Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus.". Curr. Biol. 12 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00650-9. PMID 11790298.
- Strässer K, Masuda S, Mason P, et al. (2002). "TREX is a conserved complex coupling transcription with messenger RNA export.". Nature 417 (6886): 304–8. doi:10.1038/nature746. PMID 11979277.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Lehner B, Semple JI, Brown SE, et al. (2004). "Analysis of a high-throughput yeast two-hybrid system and its use to predict the function of intracellular proteins encoded within the human MHC class III region.". Genomics 83 (1): 153–67. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(03)00235-0. PMID 14667819.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs.". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Pryor A, Tung L, Yang Z, et al. (2004). "Growth-regulated expression and G0-specific turnover of the mRNA that encodes URH49, a mammalian DExH/D box protein that is highly related to the mRNA export protein UAP56.". Nucleic Acids Res. 32 (6): 1857–65. doi:10.1093/nar/gkh347. PMC 390356. PMID 15047853. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=390356.
- Leaw CL, Ren EC, Choong ML (2004). "Hcc-1 is a novel component of the nuclear matrix with growth inhibitory function.". Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 61 (17): 2264–73. doi:10.1007/s00018-004-4205-x. PMID 15338056.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Andersen JS, Lam YW, Leung AK, et al. (2005). "Nucleolar proteome dynamics.". Nature 433 (7021): 77–83. doi:10.1038/nature03207. PMID 15635413.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network.". Nature 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Kapadia F, Pryor A, Chang TH, Johnson LF (2007). "Nuclear localization of poly(A)+ mRNA following siRNA reduction of expression of the mammalian RNA helicases UAP56 and URH49.". Gene 384: 37–44. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2006.07.010. PMID 16949217.
- Sugiura T, Sakurai K, Nagano Y (2007). "Intracellular characterization of DDX39, a novel growth-associated RNA helicase.". Exp. Cell Res. 313 (4): 782–90. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.11.014. PMID 17196963.
PDB gallery Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 19 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.