- DPP6
-
Dipeptidyl-peptidase 6 
PDB rendering based on 1xfd.Available structures PDB 1xfd Identifiers Symbols DPP6; DPPX; FLJ55680; MGC46605; VF2 External IDs OMIM: 126141 MGI: 94921 HomoloGene: 22560 GeneCards: DPP6 Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • serine-type peptidase activity
• dipeptidyl-peptidase activityCellular component • membrane
• integral to membraneBiological process • proteolysis
• cell deathSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 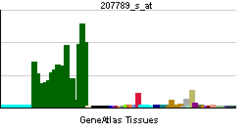
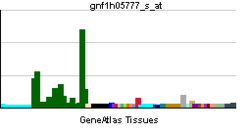
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 1804 13483 Ensembl ENSG00000130226 ENSMUSG00000061576 UniProt P42658 Q5U4C2 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001039350.1 NM_010075 RefSeq (protein) NP_001034439.1 NP_034205 Location (UCSC) Chr 7:
153.58 – 154.69 MbChr 5:
27.14 – 28.05 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Dipeptidyl aminopeptidase-like protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DPP6 gene.[1][2]
This gene encodes a single-pass type II membrane protein that is a member of the S9B family in clan SC of the serine proteases. This protein has no detectable protease activity, most likely due to the absence of the conserved serine residue normally present in the catalytic domain of serine proteases. However, it does bind specific voltage-gated potassium channels and alters their expression and biophysical properties. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized.[2]
References
- ^ Wada K, Yokotani N, Hunter C, Doi K, Wenthold RJ, Shimasaki S (Feb 1992). "Differential expression of two distinct forms of mRNA encoding members of a dipeptidyl aminopeptidase family". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89 (1): 197–201. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.1.197. PMC 48203. PMID 1729689. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=48203.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: DPP6 dipeptidyl-peptidase 6". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1804.
Further reading
- Adams MD, Kerlavage AR, Fleischmann RD, et al. (1995). "Initial assessment of human gene diversity and expression patterns based upon 83 million nucleotides of cDNA sequence." (PDF). Nature 377 (6547 Suppl): 3–174. PMID 7566098. http://www.columbia.edu/itc/biology/pollack/w4065/client_edit/readings/nature377_3.pdf.
- Yokotani N, Doi K, Wenthold RJ, Wada K (1993). "Non-conservation of a catalytic residue in a dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV-related protein encoded by a gene on human chromosome 7.". Hum. Mol. Genet. 2 (7): 1037–9. doi:10.1093/hmg/2.7.1037. PMID 8103397.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery.". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- "Toward a complete human genome sequence.". Genome Res. 8 (11): 1097–108. 1999. doi:10.1101/gr.8.11.1097. PMID 9847074.
- Kin Y, Misumi Y, Ikehara Y (2001). "Biosynthesis and characterization of the brain-specific membrane protein DPPX, a dipeptidyl peptidase IV-related protein.". J. Biochem. 129 (2): 289–95. PMID 11173531.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Nadal MS, Ozaita A, Amarillo Y, et al. (2003). "The CD26-related dipeptidyl aminopeptidase-like protein DPPX is a critical component of neuronal A-type K+ channels.". Neuron 37 (3): 449–61. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(02)01185-6. PMID 12575952.
- Hillier LW, Fulton RS, Fulton LA, et al. (2003). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 7.". Nature 424 (6945): 157–64. doi:10.1038/nature01782. PMID 12853948.
- Schmitt-Ulms G, Hansen K, Liu J, et al. (2005). "Time-controlled transcardiac perfusion cross-linking for the study of protein interactions in complex tissues.". Nat. Biotechnol. 22 (6): 724–31. doi:10.1038/nbt969. PMID 15146195.
- Strop P, Bankovich AJ, Hansen KC, et al. (2004). "Structure of a human A-type potassium channel interacting protein DPPX, a member of the dipeptidyl aminopeptidase family.". J. Mol. Biol. 343 (4): 1055–65. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.09.003. PMID 15476821.
- Zagha E, Ozaita A, Chang SY, et al. (2005). "DPP10 modulates Kv4-mediated A-type potassium channels.". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (19): 18853–61. doi:10.1074/jbc.M410613200. PMID 15671030.
- Radicke S, Cotella D, Graf EM, et al. (2005). "Expression and function of dipeptidyl-aminopeptidase-like protein 6 as a putative beta-subunit of human cardiac transient outward current encoded by Kv4.3.". J. Physiol. (Lond.) 565 (Pt 3): 751–6. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2005.087312. PMC 1464568. PMID 15890703. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1464568.
- Ren X, Hayashi Y, Yoshimura N, Takimoto K (2005). "Transmembrane interaction mediates complex formation between peptidase homologues and Kv4 channels.". Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 29 (2): 320–32. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2005.02.003. PMID 15911355.
- Jerng HH, Kunjilwar K, Pfaffinger PJ (2006). "Multiprotein assembly of Kv4.2, KChIP3 and DPP10 produces ternary channel complexes with ISA-like properties.". J. Physiol. (Lond.) 568 (Pt 3): 767–88. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2005.087858. PMC 1464192. PMID 16123112. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1464192.
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes.". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1356129.
- Nadal MS, Amarillo Y, Vega-Saenz de Miera E, Rudy B (2006). "Differential characterization of three alternative spliced isoforms of DPPX.". Brain Res. 1094 (1): 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.03.106. PMID 16764835.
PDB gallery Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 7 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.