- Uterine malformation
-
Uterine malformation Classification and external resources 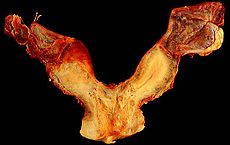
A human bicornuate uterusICD-10 Q51 ICD-9 752.2-752.3 A uterine malformation is a type of female genital malformation resulting from an abnormal development of the Müllerian duct(s) during embryogenesis. Symptoms range from amenorrhea, infertility, recurrent pregnancy loss, and pain, to normal functioning depending on the nature of the defect.
Contents
Prevalence
The prevalence of uterine malformation is estimated to be 6.7% in the general population, slightly higher (7.3%) in the infertility population, and significantly higher in a population of women with a history of recurrent miscarriages (16%).[1]
Types
The American Fertility Society (now American Society of Reproductive Medicine) Classification distinguishes:
- Class I: Müllerian agenesis (absent uterus).
- Uterus is not present, vagina only rudimentary or absent. The condition is also called Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome. The patient with MRKH syndrome will have primary amenorrhea.
- Class II: Unicornuate uterus (a one-sided uterus).
- Only one side of the Müllerian duct forms. The uterus has a typical "penis shape" on imaging systems.
- Class III: Uterus didelphys, also uterus didelphis (double uterus).
- Both Müllerian ducts develop but fail to fuse, thus the patient has a "double uterus". This may be a condition with a double cervix and a vaginal partition (v.i.), or the lower Müllerian system fused into its unpaired condition. See Triplet-birth with Uterus didelphys for a case of a woman having spontaneous birth in both wombs with twins.
- Class IV: Bicornuate uterus (uterus with two horns).
- Only the upper part of that part of the Müllerian system that forms the uterus fails to fuse, thus the caudal part of the uterus is normal, the cranial part is bifurcated. The uterus is "heart-shaped".
- Class V: Septated uterus (uterine septum or partition).
- The two Müllerian ducts have fused, but the partition between them is still present, splitting the system into two parts. With a complete septum the vagina, cervix and the uterus can be partitioned. Usually the septum affects only the cranial part of the uterus. A uterine septum is the most common uterine malformation and a cause for miscarriages. It is diagnosed by medical image techniques, i.e. ultrasound or an MRI. MRI is considered the preferred modality due to its multiplanar capabilities as well as its ability to evaluate the uterine contour, junctional zone, and other pelvic anatomy. A hysterosalpingogram is not considered as useful due to the inability of the technique to evaluate the exterior contour of the uterus and distinguish between a bicornuate and septate uterus.
A uterine septum can be corrected by hysteroscopic surgery.
- Class VI: DES uterus.
- The uterine cavity has a "T-shape" as a result of fetal exposure to diethylstilbestrol.
An additional variation is the arcuate uterus where there is a concave dimple in the uterine fundus within the cavity.
A rudimentary uterus is a uterine remnant not connected to cervix and vagina and may be found on the other side of an unicornuate uterus.
Patients with uterine abnormalities may have associated renal abnormalities including unilateral renal agenesis.[2]
"Double vagina"
As the vagina is largely derived from the Müllerian ducts, lack of fusion of the two ducts can lead to the formation of a vaginal duplication and lack of absorption of the wall between the two ducts will leave a residual septum, leading to a "double vagina". This condition may be associated with a uterus didelphys or a uterine septum.[3][4][5] Since the condition is internal and usually asymptomatic, a person may not be aware of having a "double vagina." If necessary, the partition can be surgically corrected, however, there is no valid medical reason for such a procedure.
Diagnosis
Besides a physical examination, the physician will need imaging techniques to determine the character of the malformation: gynecologic ultrasonography, pelvic MRI, or hysterosalpingography. A hysterosalpingogram is not considered as useful due to the inability of the technique to evaluate the exterior contour of the uterus and distinguish between a bicornuate and septate uterus. In addition, laparoscopy and/or hysteroscopy may be indicated. In some patients the vaginal development may be affected.
Treatment
Surgical intervention depends on the extent of the individual problem. With a didelphic uterus surgery is not usually recommended. A uterine septum can be resected in a simple out-patient procedure that combines laparoscopy and hysteroscopy. This procedure greatly decreases the rate of miscarriage for women with this anomaly.
References
- ^ Sotirios H. Saravelos, Karen A. Cocksedge and Tin-Chiu Li (2008). "Prevalence and diagnosis of congenital uterine anomalies in women with reproductive failure: a critical appraisal.". Human Reproduction Update 14 (5): 415–29. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmn018. PMID 18539641.[1]
- ^ Li, S; Qayyum, A; Coakley, FV; Hricak, H (2000). "Association of renal agenesis and mullerian duct anomalies.". Journal of computer assisted tomography 24 (6): 829–34. doi:10.1097/00004728-200011000-00001. PMID 11105695.
- ^ Heinonen, PK (2006). "Complete septate uterus with longitudinal vaginal septum.". Fertility and sterility 85 (3): 700–5. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2005.08.039. PMID 16500341.
- ^ Perez-Brayfield, MR; Clarke, HS; Pattaras, JG (2002). "Complete bladder, urethral, and vaginal duplication in a 50-year-old woman.". Urology 60 (3): 514. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(02)01808-3. PMID 12350504.
- ^ British Woman With 2 Wombs Has Triplets. Associated Press, 22 December 2006.
External links
Female congenital anomalies of the genitalia, including Intersex and DSD: (Q50–Q52 · 752.0–752.4) Internal Uterine malformationExternal Categories:- Congenital disorders of female genital organs
- Class I: Müllerian agenesis (absent uterus).
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
