- Copper-copper(II) sulfate electrode
-
The Copper-copper(II) sulfate electrode is a reference electrode of the first kind[1], based on the redox reaction with participation of the metal (copper) and its salt - copper(II) sulfate. It is used for measuring electrochemical potential and is the most commonly used reference electrode for testing cathodic protection corrosion control systems[2].
The corresponding equation can be presented as follow:
- Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu0(metal)
This reaction characterized by reversible and fast electrode kinetics[3], meaning that a sufficiently high current can be passed through the electrode with the 100% efficiency of the redox reaction (dissolution of the metal or cathodic deposition of the copper-ions).
The Nernst equation below shows the dependence of the potential of the copper-copper(II) sulfate electrode on the activity or concentration copper-ions:
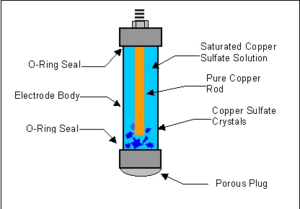
Commercial reference electrodes consist of a plastic tube holding the copper rod and saturated solution of copper sulfate. A porous plug on one end allows contact with the copper sulfate electrolyte. The copper rod protrudes out of the tube. A voltmeter negative lead is connected to the copper rod.
The potential of a copper copper sulfate electrode is +0.314 volt with respect to the standard hydrogen electrode.
Applications
- Cathodic Protection
- Copper coulometer
- Copper-copper(II) sulfate electrode is also used as a one of the half cell in the Daniel-Jakobi galvanic cell.
Notes
References
- E. Protopopoff and P. Marcus, Potential Measurements with Reference Electrodes, Corrosion: Fundamentals,
Testing, and Protection, Vol 13A, ASM Handbook, ASM International, 2003, p 13-16
- A.W. Peabody, Peabody's Control of Pipeline Corrosion, 2nd Ed., 2001, NACE International. ISBN 1575900920
Categories:- Electrodes
- Corrosion prevention
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.