- Gravitational anomaly
-
In theoretical physics, a gravitational anomaly is an example of a gauge anomaly: it is an effect of quantum mechanics–usually a one-loop diagram—that invalidates the general covariance of a theory of general relativity combined with some other fields. The adjective "gravitational" is derived from the symmetry of a gravitational theory, namely from general covariance. It is also known as diffeomorphism anomaly, since general covariance is symmetry under coordinate reparametrization; i.e. diffeomorphism.
General covariance is the basis of general relativity, the current theory of gravitation. Moreover, it is necessary for the consistency of any theory of quantum gravity, since it is required in order to cancel unphysical degrees of freedom with a negative norm, namely gravitons polarized along the time direction. Therefore all gravitational anomalies must cancel out.
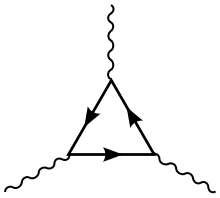
The anomaly usually appears as a Feynman diagram with a chiral fermion running in the loop (a polygon) with n external gravitons attached to the loop where n = 1 + D / 2 where D is the spacetime dimension. Anomalies occur only in even spacetime dimensions. However, anomalies can occur in the case of an odd dimensional spacetime manifold with boundary.
See also
- For a different concept in geodesy and geophysics, dealing with differences between observed values of gravity and predicted values for that location, see gravity anomaly.
- mixed anomaly
- Green-Schwarz mechanism
References
- Alvarez-Gaume, Luis; Edward Witten (1984). "Gravitational Anomalies". Nucl. Phys. B 234 (2): 269. Bibcode 1984NuPhB.234..269A. doi:10.1016/0550-3213(84)90066-X.
Quantum gravity Central concepts graviton · Planck scale · trans-Planckian problem · quantum foam · AdS/CFT correspondence · IR/UV mixing · causal patch · gravitational anomaly · Weinberg–Witten theoremBlack holes black hole thermodynamics · black hole information paradox · holographic principle · Bousso's holographic bound · black hole complementarity · gravitational singularityQuantum field theory
in curved spacetimeProposed theories canonical quantum gravitysuperfluid vacuum theoryLogarithmic BEC vacuumothersToy models 2+1D topological gravity · CGHS model · RST model · Liouville gravity · type 0 string theory · Jackiw–Teitelboim gravityApplications Others quantum mechanics of time travelCategories:- Quantum physics stubs
- Anomalies in physics
- Quantum gravity
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.