- A Million Random Digits with 100,000 Normal Deviates
-
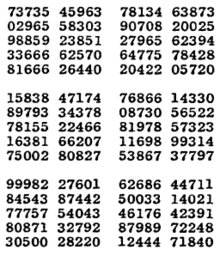
A Million Random Digits with 100,000 Normal Deviates is a 1955 book by the RAND Corporation. The book, consisting primarily of a random number table, was an important 20th century work in the field of statistics and random numbers. It was produced starting in 1947 by an electronic simulation of a roulette wheel attached to a computer, the results of which were then carefully filtered and tested before being used to generate the table. The RAND table was an important breakthrough in delivering random numbers, because such a large and carefully prepared table had never before been available. In addition to being available in book form, one could also order the digits on a series of punched cards. The main use of the tables was in statistics and the experimental design of scientific experiments, especially those which employed the Monte Carlo method; in cryptography, they have also been used as "nothing up my sleeve numbers", for example in the design of the Khafre cipher. The book was one of the last of a series of random number tables produced from the mid-1920s through the 1950s, after which the development of high speed computers allowed faster operation through the generation of pseudorandom numbers rather than reading them from tables. The book was reissued in 2001 (ISBN 0-8330-3047-7) with a new foreword by RAND Executive Vice President Michael D. Rich. It has generated many humorous user reviews on Amazon.com.[1][2][3] The digits and the deviates are available for free online, at: Datafile: A Million Random Digits and 100,000 Normal Deviates. The text of the book is also available at [1]. They begin:
References
- ^ Amazon.com Customer Reviews: A Million Random Digits with 100,000 Normal Deviates (Paperback version)]
- ^ Heffernan, Virginia (January 15, 2010). "The Reviewing Stand". The New York Times Magazine. http://www.nytimes.com/2010/01/17/magazine/17FOB-Medium-t.html. Retrieved 2011-03-09.
- ^ Swaine, Michael (2005). "Is the Future Random and Faceless?". Dr Dobbs Journal 30: 95. http://drdobbs.com/open-source/184406045.
- George W. Brown, "History of RAND's random digits—Summary," in A.S. Householder, G.E. Forsythe, and H.H. Germond, eds., Monte Carlo Method, National Bureau of Standards Applied Mathematics Series, 12 (Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1951): 31-32. (Available here for download from the RAND Corporation.)
External links
Categories:- 1955 books
- Randomness
- Statistics books
- Mathematics books
- RAND Corporation
- Mathematical tables
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.