- Urban density
-
Urban density is a term used in urban planning and urban design to refer to the number of people inhabiting a given urbanized area. As such it is to be distinguished from other measures of population density. Urban density is considered an important factor in understanding how cities function. Research related to urban density occurs across diverse areas, including economics, health, innovation, psychology and geography as well as sustainability.
Contents
Urban density and sustainability
It is commonly asserted that higher density cities are more sustainable than low density cities. Much planning theory, particularly in North America, the UK, Australia and New Zealand has been developed premised on raising urban densities, such as New Urbanism, Transit-oriented development, and Smart growth.
However, the link between urban density and aspects of sustainability remains a contested area of planning theory[citation needed]. Many[who?] experts on sustainable urbanism, including prominent urban designer Jan Gehl, argue that low-density, dispersed cities are unsustainable as they are automobile dependent. Others, like Randy O'Toole author of Gridlock and a senior fellow at the Cato Institute, counter that raising densities results in more expensive real estate, greater road congestion and more air pollution. At a broader level though, there is evidence to indicate a strong negative correlation between the total energy consumption of a city and its overall urban density, i.e. the lower the density, the more energy consumed.[1]
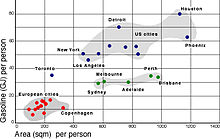
Measuring urban density
Urban density is a very specific measurement of the population of an urbanized area, excluding non-urban land-uses. Non-urban uses include regional open space, agriculture and water-bodies.
There are a variety of other ways of measuring the density of urban areas:
- Floor area ratio - the total floor area of buildings divided by land area of the lot they are built on
- Residential density - the number of dwelling units in any given area
- Population density - the number of people in any given area
- employment density - the number of jobs in any given area
- Gross density - any density figure for a given area of land that includes uses not necessarily directly relevant to the figure (usually roads and other transport infrastructure)
- Net density - a density figure for a given area of land that excludes land not directly related to the figure.
- Weighted density - a density metric which measures the density at which the average citizen lives. It is determined by calculating the standard density of each census tract, assigning each a weight equal to its share of the total population, and then adding the segments.
See also
Footnotes
References
- Urban Density and Energy Consumption
- Deriving urban density in Greater Washington DC
- The Value of Density, New Zealand government website
- EPA website, Urbanization Indicator Descriptions
- 'The cost of smart growth revisited: Consumer expenditures lower where sprawl is greater' Demographia website
- Newman, P and Kenworthy, J (1999) Cities and Sustainability: Overcoming automobile dependence, Washington, D. C. : Island Press ISBN 1559636602
- Mees, P. (2000) A Very Public Solution: public transport in the dispersed city, Carlton South, Vic: Melbourne University Press (ISBN 0522848672)
- Metricity, Measures of Urban Density Study
- 'Weighted Density'
External links
Supportive views
Critical views
Categories:- Urban studies and planning
- Sustainable development
- Demography
- Population
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.