- Atlantic tripletail
Taxobox | name = Atlantic tripletail
image_width = 240px
regnum =Animalia
phylum =Chordata
classis =Actinopterygii
ordo =Perciformes
familia =Lobotidae
genus = "Lobotes "
species = "L. surinamensis"
binomial = "Lobotes surinamensis"
binomial_authority = (Bloch, 1790)The Atlantic tripletail, "Lobotes surinamensis", is a warm water marine
fish that can grow to 90 cm long and weigh 18 kg. It is also known under the name "flasher". [ [http://www.fishbase.org/ComNames/CommonNameSummary.cfm?autoctr=23667 FishBase Common Names] ]Geographical distribution
The Atlantic tripletail is the only fish in the
Lobotidae family that can be found in the Atlantic Ocean.Atlantic tripletails are found from
Massachusetts andBermuda toArgentina , the easternAtlantic andMediterranean Sea , fromMadeira Island to theGulf of Guinea , the easternPacific fromCosta Rica toPeru , and the western Pacific fromJapan toFiji andTuvalu . They are rarely found north ofChesapeake Bay . They are found on theGulf Coast from April to October and then migrate to warmer waters during winter.Habitat
Atlantic tripletails are found coastally in most, but not all, tropical and subtropical seas. They are semi-migratorial and
pelagic . Normally solitary, they have been known to form schools. They can be found in bays, sounds, and estuaries during the summer. Juveniles are usually found swimming under patches of "Sargassum " algae. Adults are usually found in the waters of theGulf of Mexico but can also be found in passes, inlets, and bays near river mouths. The fishes are also often found in or near shipwrecks, beams or supports, jetties, and sea buoys. Larvae are usually found in waters that exceed temperatures of 84 °F (29 °C), greater than 30.3‰ salinity, and more than 230 feet (70 m) deep.Biology
Distinctive features
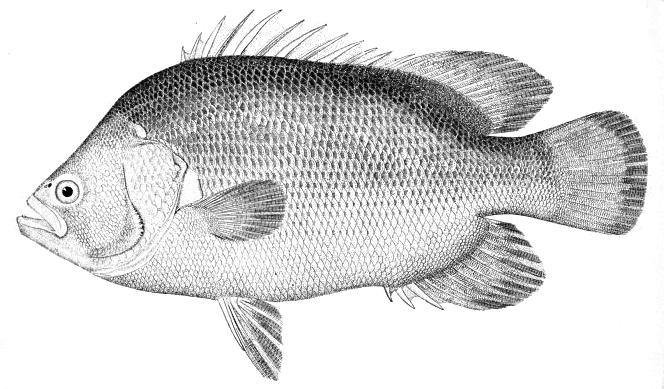
Atlantic tripletails have scales that extend onto the dorsal, anal, and
caudal fin s and a head profile that concaves as the fish ages. It has a compressed but deep body with a triangle-shaped head. The eyes are small but the mouth is large. The bases of the dorsal and anal fins are scaled and thepectoral fin s are shorter than the pelvic fins. The name "tripletail" is given because of the fish's three rounded fins: dorsal, caudal, and anal.Coloration
Juvenile Atlantic tripletails are colored a mottled yellow, brown, and black. Adults are jet black. When it lies on its side at the surface, the tripletail is sometimes confused for a floating mangrove leaf. The juveniles have white pectoral fins and a white margin on the caudal fin. Adult tripletails have varied mottled color patterns which range from dark brown to reddish brown, often with a tint of gray.
Size, age, and growth
The Atlantic tripletail grows to 35 inches (89 cm) in length and weighs up to 41 pounds
Diet
Atlantic tripletails are opportunistic eaters. This means that they feed on a variety of things, mostly small finfish like
gulf menhaden ,Atlantic bumpersss , and anchovies. They also feed oninvertebrate s likeblue crab s andbrown shrimp , as well as otherbenthic crustacean s.Reproduction
Spawning primarily occurs in the summer along both the Atlantic and the U.S. Gulf of Mexico coasts, with peaks during the months of July and August. Large congregations of tripletail during the summer months in the inshore and nearshore waters of coastal Georgia suggest that this area is a critical estuarian spawning habitat for the species. Larval Atlantic tripletails go though four levels of development; preflexion, flexion, postflexion, and transformation. By the time the larvae reach 0.16 inches (4 mm), they have large eyes and a concave head. The larval forms of Atlantic tripletails resemble those of
boarfish es, some jacks,spadefish es andbigeye s.Predators
Atlantic tripletails do not have many predators, but the main ones are
shark s and largerteleost s.Parasites
Parasites that affect the tripletail include the
copepod s "Anuretes heckelii " which affect the branchial cavities, "Lernanthropus pupa " which affect the gill filaments, and "Scianophilus tenius ".Importance to humans
A few tons of Atlantic tripletails are fished commercially on the east and west coasts of
Florida , and marketed fresh, frozen, or salted. They are mainly caught usinghaul seine s,gill net s and line gear. They are common indriftnet catches oftuna along the edge of the continental shelf. This fish is infrequently targeted by recreational fishers.Conservation
The Atlantic tripletail is not listed as endangered or vulnerable with the World Conservation Union (IUCN). The IUCN is a global union of states, governmental agencies, and non-governmental organizations in a partnership that assesses the conservation status of species.
References
Most of the information in this article was written by Tina Perrotta in an article for the Icthyology branch of the
Florida Museum of National History .
*
*
*
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
