- BamHI
-
BamHI 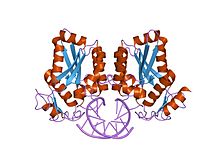
restriction endonuclease bamhi bound to a non-specific dna. Identifiers Symbol BamHI Pfam PF02923 Pfam clan CL0236 InterPro IPR004194 SCOP 1bhm Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary BamHI is a restriction enzyme, derived from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. It has the recognition site (G'GATCC), and leaves a sticky end.[1][2][3] One of the earlier enzymes to be used, it is popular for historical reasons, but also because digestion leaves a GATC overhang compatible with many other enzymes. Persistent issues with this specific enzyme spontaneously failing to generate cloneable fragments necessitate aliquoting prior to use. Engineered variants of the enzyme have been created in order to avoid star activity.
Recognition site
G G A T C C C C T A G G
As at the end of 2010, there were 5 crystal structures of BamH1 in the Protein Data Bank
References
- ^ Molecular cell biology. Lodish, Harvey F. 5. ed. : - New York : W. H. Freeman and Co., 2003, 973 s. b ill. ISBN 0-7167-4366-3
- ^ Newman M, Strzelecka T, Dorner LF, Schildkraut I, Aggarwal AK (April 1994). "Structure of restriction endonuclease BamHI and its relationship to EcoRI". Nature 368 (6472): 660â4. doi:10.1038/368660a0. PMID 8145855.
- ^ Viadiu H, Aggarwal AK (May 2000). "Structure of BamHI bound to nonspecific DNA: a model for DNA sliding". Mol. Cell 5 (5): 889â95. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80329-9. PMID 10882125.
External links
This article includes text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR004194
Categories:- Molecular biology
- Biotechnology
- Restriction enzymes
- Molecular and cellular biology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
