- Nebettawy
-
Nebettawy Queen consort of Egypt 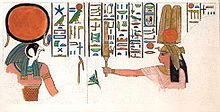
Nebettawy before the God Horus as depicted in her tomb.Full name Nebettawy Titles Great Royal Wife
Lady of The Two Lands
Mistress of Upper and Lower Egypt, etcConsort Ramesses II Dynasty 19th Dynasty of Egypt Father Ramesses II Mother Queen Nefertari ? Religious beliefs Ancient Egyptian religion ![V30 [nb] nb](/w/extensions/wikihiero/img/hiero_V30.png)
![X1 [t] t](/w/extensions/wikihiero/img/hiero_X1.png)



Nebettawy
in hieroglyphsNebettawy (nb.t-t3.wỉ; “Lady of the Two Lands”) was an Ancient Egyptian princess and queen, the fifth daughter and one of the eight Great Royal Wives of Pharaoh Ramesses II.
Contents
Life
Nebettawy may have been the daughter of Ramesses' most beloved wife, Nefertari[1] [2], but this is by no means certain. She is shown in the greater Abu Simbel temple. On the second southern colossus in front of the temple Nebettawy is depicted in the regalia of a queen. Nebettawy shown with a cap wig, a fairly simple modius and the double plumes. Bint-Anath (also dressed as a queen) stands by the left leg of the second southern colossus, Nebettawy by the right leg, and princess Isetnofret II stands in front of the colossus.[3]
Nebettawy appears as the fifth princess in a parade of royal daughters as depicted in the great temple at Abu Simbel. She appears behind Bintanath, Bakmut, Nefertari, and Meritamen. The princesses are shown carrying a sistrum.[1]
Nebettawy is not shown on the smaller temple of Abu Simbel. Nefertari is shown with Meytamen and Henuttawy on the facade of this temple.[4]
After Bintanath and Meritamen, she was the third of Ramesses' daughters to become her father's wife (possibly after the death of Meritamen). Nebettawy served as Great Royal Wife while her father entered the diplomatic marriage with Maathorneferure, the daughter of the Hittite king Hattusilis III, in year 33. Nebettawy and her half-sister Bintanath fulfilled the ritual role of that of the queen of Egypt.[3] She held the titles Lady of the Two Lands (nb.t-t3.wỉ), Great Royal Wife (ḥm.t-nsw wr.t), Mistress of Upper and Lower Egypt (ḥnw.t šmˁw mḥw), King’s Daughter (s3.t-nsw), King’s Daughter of his body, his beloved (s3.t-nsw n.t ẖt=f mrỉỉ.t=f).[5]
Death and Burial
She was buried in the tomb QV60.[1] The tomb was robbed already in antiquity and was later used as a Christian chapel.[3] In one of the scenes in the tomb, Nebettawy wears a rather special headdress: a vulture crown with uraeus, topped by a modius and supporting a number of flowers. This specific headdress is only attested for Queen Nebettawy, Queen Isis (QV51 - time of Ramesses III-IV) and Queen Tyti (QV52 - 20th dynasty). It is not known what the precise meaning of this piece of regalia was. An earlier version of this crown was worn by Princess-Queen Sitamen, the daughter-wife of Amenhotep III. Hence it could be a reference to her position as Princess-Queen. [6]
Sources
- ^ a b c Dodson, Aidan and Hilton, Dyan. The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt. Thames & Hudson. 2004. ISBN 0-500-05128-3
- ^ Tyldesley, Joyce. Chronicle of the Queens of Egypt. Thames & Hudson. 2006. ISBN 0-500-05145-3
- ^ a b c Tyldesley, Joyce. Ramesses: Egypt's Greatest Pharaoh. Penguin. 2001. ISBN 0140280979
- ^ Kitchen, K.A., Rammeside Inscriptions, Translated & Annotated, Translations, Volume II, Blackwell Publishers, 1996
- ^ Grajetzki, Ancient Egyptian Queens: A Hieroglyphic Dictionary, Golden House Publications, London, 2005, ISBN 978-0954721893
- ^ van Sicklen: A Ramesside Ostracon of Queen Isis; Journal of Near Eastern Studies 1974
External links
Categories:- 13th-century BC women
- Ancient Egyptian queens consort
- Nineteenth dynasty of Egypt
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
