- Charles Redheffer
-
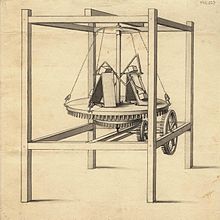
Charles Redheffer was an American inventor who claimed to have invented a perpetual motion machine. First appearing in Philadelphia, Redheffer exhibited his machine to the public, charging high prices for viewing. When he applied to the government for more money, a group of inspectors were sent to examine the machine. It was discovered the machine was actually powered by a device Redheffer claimed was powered by the machine.
Redheffer moved to New York City and set up a similar scam after rebuilding his machine. However, an engineer could detect it was a fake when he visited an exhibition by listening to its unsteady motions. He discovered that the machine was operated by a man using a crank in a room on the floor above. Redheffer returned to Philadelphia. He later claimed to have created another machine, but refused to demonstrate it to anyone. He managed to get a patent for his machine in 1820, but after this his fate is unknown.
Contents
Personal life
Little has been recorded about Redheffer's life, other than his connection to the hoax. According to one source, he was from Germantown in Philadelphia,[1] but most sources simply state that he appeared in Philadelphia with his machine. Redheffer disappeared from public view after the discovery of the fraud, and his fate is unknown.
Appearance in Philadelphia
Charles Redheffer and his machine became well known in Philadelphia in 1812.[2] Redheffer claimed he had invented a perpetual motion machine and exhibited it in a house near the Schuylkill River in the outskirts of the city.[3] He charged an admission fee of $5 (some sources claim $1) for men to view it; depending on the source, women were admitted free or at a charge of $1.[4][5] The machine caused a sensation, and Redheffer lobbied for funds to build a larger version.[3]
On January 21, 1813, eight city commissioners visited Redheffer to inspect the machine. They had to do so through a barred window,[3] as Redheffer was concerned anyone going near the machine might damage it.[6] One of the inspectors, Nathan Sellers, was accompanied by his son Coleman, who noticed something odd about the gears. The machine itself was said to be powering a separate device through a series of gears and weights. Coleman noticed that the cogs were worn on the wrong side and suggested that the device was in fact powering the machine.[7]
The elder Sellers was convinced the machine was a hoax. To validate his suspicions, he hired local engineer Isaiah Lukens to build a similar machine, using a hidden clockwork motor as a power source.[8] They then arranged a demonstration of the machine to Redheffer, who was immediately convinced and offered to buy it.[7] Meanwhile, Redheffer's machine appeared in the Philadelphia Gazette. Civil engineer Charles Gobort offered to bet sums of money ranging from $6,000 to $10,000 that the machine was genuine, and that Redheffer had discovered perpetual motion.[7]
Move to New York City
His ruse revealed, Redheffer immediately departed for New York City where he was still unknown.[6] He changed his machine somewhat so that it could not be detected as easily, and he exhibited it as he had done in Philadelphia.[9]
When mechanical engineer Robert Fulton went to see the machine, he noticed that the machine was unsteady as if someone would have powered it manually and irregularly with a crank.[6] Fulton also detected that the sound was uneven, uncharacteristic of a machine's motions. He announced the machine was a fraud, and challenged Redheffer exclaiming he would expose the secret power source, otherwise he would pay for all the damage he would cause. Redheffer agreed, so Fulton removed some boards from the wall alongside the machine and exposed a catgut cord that led to the upper floor. Upstairs he found an old man who was turning a hand-crank with one hand and eating bread with the other. Spectators realized they had been duped and destroyed the machine; Redheffer fled the city.[7]
Later appearances
Redheffer appears to have constructed another machine in 1816, which he stated his intention to demonstrate to a group of men including the mayor and chief justice of Philadelphia. However, despite several meetings, Redheffer refused to demonstrate the machine to them.[10] By 1820, he managed to obtain a patent for his machine, which was described as "power, machinery for the purpose of gaining".[11]
Notes
- ^ Weiss, p.35
- ^ Ord-Hume, p.125
- ^ a b c Ord-Hume, p.126
- ^ Ord-Hume, p.130
- ^ "The Puzzle of Perpetual Motion". The Sydney Morning Herald (Fairfax Media): pp. 8. 26 July 1954.
- ^ a b c "Perpetual Motion Machine of Charles Redheffer". Museum of Hoaxes. http://www.museumofhoaxes.com/hoax/Hoaxipedia/Perpetual_Motion_Machine_of_Charles_Redheffer/. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ a b c d Hicks, Clifford B. (April 1961). "Why won’t they work?". American Heritage Magazine (American Heritage Publishing Company). http://www.americanheritage.com/articles/magazine/ah/1961/3/1961_3_78.shtml. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ Ord-Hume, p.127
- ^ Ord-Hume, p.132
- ^ Ogden-Niles, p.26-27
- ^ Force, p.145
References
- Force, Peter (1821). A National Calendar ... Volume 2. Davis and Force.
- Ogden Niles, William (1817). Niles' weekly register, Volume 11. H. Niles.
- Ord-Hume, Arthur W. J. G. (2006). Perpetual Motion: The History of an Obsession. Adventures Unlimited Press. ISBN 9781931882514.
- Weiss, Harry B.; Ziegler, Grace M. (1978). Thomas Say, early American naturalist. Ayer Publishing. ISBN 9780405107375.
Categories:- Hoaxes in science
- Perpetual motion
- Hoaxes in the United States
- 19th-century hoaxes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.