- Chronic cystic mastitis
Infobox_Disease
Name = Chronic cystic mastitis
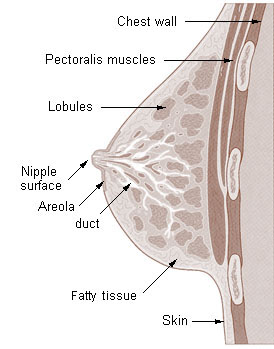
Caption = Cross section of the breast of an adult, female human.
DiseasesDB = 4799
ICD10 = ICD10|N|60|1|n|60
ICD9 = ICD9|610.1
ICDO =
OMIM =
MedlinePlus = 000912
eMedicineSubj =
eMedicineTopic =
MeshID = D005348Chronic cystic mastitis, also called fibrocystic disease, Diffuse cystic mastopathy and Mammary dysplasia is a condition rather than a disease. An estimated 30-60% of women suffer from this condition. It is characterized by noncancerous lumps in the breast.Nevertheless, it can be organised into the
Mastitis spectrum.ymptoms
Chronic Cystic Mastitis is characterised by the appearance of
fibrous tissue and a lumpy,cobblestone texture in the breasts. These lumps are smooth with defined edges, and are usually free-moving in regard to adjacent structures. The bumps can sometimes be obscured by irregularities in the breast that are associated with the condition. The lumps are most often found in the upper, outer sections of the breast (nearest to thearmpit ). Women with Chronic Cystic Mastitis may experience a persistent or intermittent aching in their breasts related to periodic swelling. Breasts andnipples may be tender oritchy .Symptoms follow a periodic trend tied closely to themenstrual cycle . Symptoms tend to peak immediately before each period and decrease afterwards. At peak, breasts may feel full and swollen. No complications related tobreastfeeding have been found.Causes
The causes of the condition are not fully understood, though it is known that they are tied to
ovarian hormone levels, as the condition usually subsides aftermenopause . It is also related to the menstrual cycle and to dietary conditions. The incidence is lower in women takingbirth control , possibly because of the regulation of hormone levels. Dietaryfat levels andcaffeine intake may have an effect on the onset of the condition, as may family history.Diagnosis and Treatment
This condition is often easily diagnosed by a doctor, though it may require a
biopsy of the affected area.Mammography does not often work for diagnosis of CCM, as the breast tissue is often too dense to allow for thorough examination.Aspiration with a very fine needle is used to drain fluid from largercyst s. There is no cure for the condition, but symptoms may be reduced by monitoring caffeine and fat intake, wearing a well fittingbra . In severe cases a syntheticandrogen may be prescribed.Prognosis
There are usually no adverse side effects to this condition. In almost all cases it subsides after menopause. A possible complication arises through the fact that
cancerous tumors may be more difficult to detect in women with CCM. This condition does not seem to lead to increased breast cancer risk. [ [http://www.cancer.org/docroot/CRI/content/CRI_2_4_2X_What_are_the_risk_factors_for_breast_cancer_5.asp?sitearea= What Are the Risk Factors for Breast Cancer] , "Breast Cancer: Detailed Guide"]ee also
*
Fibroadenoma
*Breast References
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
