- Cranial vault
-
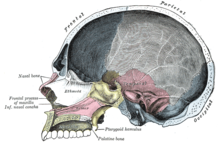 Sagittal section of a human skull, showing the cranial vault
Sagittal section of a human skull, showing the cranial vault
The cranial vault is the space in the skull within the neurocranium, occupied by the brain. In humans, the size and shape of the brain, may be affected by the size of the vault as shown in craniometry, but studies relating it to intelligence have been ambivalent. The vault is alternatively called "skullcap" or even calvaria, though these properly refer to the upper portion of the skull only.
Contents
Development
In humans, the cranial vault is imperfectly composed in newborns, to allow the large human head to pass through the birth canal. During birth, the various bones connected by cartilage and ligaments only will move relatively to each other. The open portion between the major bones of the upper part of the vault, called fontanelles, normally remain soft up to two years after birth.
As the fontanelles close, the vault loses some of its plasticity. The sutures between the bones remain until 30 to 40 years of age, allowing for growth of the brain. Cranial vault size is directly proportional to skull size and is developed early.[1]
The size and shape of the brain and the surrounding vault remain quite plastic as the brain grows in childhood. In several ancient societies, head shape was altered for aesthetic or religious reasons by binding cloth or boards tightly around the head during infancy. It is not known whether such artificial cranial deformation has an effect in mental capacity.
Evolution
 Skull of Carrion Crow, showing the enlarged vault found in birds.
Skull of Carrion Crow, showing the enlarged vault found in birds.
The cranial vault is composed of the endocranium forming the basal parts, topped by the skull roof in land vertebrates.[2]
In fishes no distinct cranial vault as such exists, the skull being composed of loosely jointed bones. The cranial vault as a distinct unit arose with the fusion of the skull roof and the endocranium on the early Labyrinthodonts.[2] In amphibians and reptiles the vault is rather small and inconspicuous, only forming proper vaults in mammals and birds.
References
- ^ "Changes in vault dimensions must occur by early childhood because of the early development of the vault." Secular change in craniofacial morphology "During the 125 years under consideration, cranial vaults have become markedly higher and somewhat narrower, with narrower faces. The changes in cranial morphology are probably in large part due to changes in growth at the cranial base due to improved environmental conditions. The changes are likely a combination of phenotypic plasticity and genetic changes over this period." Cranial change in Americans: 1850-1975.
- ^ a b Romer, A.S. & T.S. Parsons. 1977. The Vertebrate Body. 5th ed. Saunders, Philadelphia. (6th ed. 1985)
See also
Categories:- Biology terminology
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
