- Karenia brevis
Taxobox
color = khaki
name = Karenia brevis
image_width = 250px
domain = Eukaryota
regnum =Protist a
phylum =Dinophyta
classis =Dinophyceae
genus = "Karenia"
species = "K. brevis"
binomial = "Karenia brevis"
binomial_authority = (Davis) G. Hansen et Moestrup"Karenia brevis" (formerly known as "
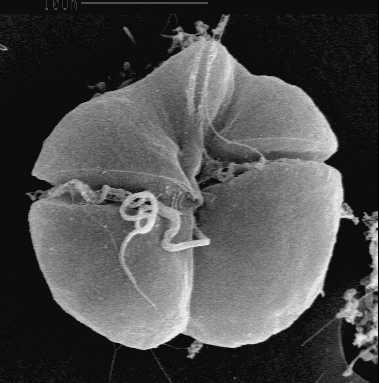
Gymnodinium breve" and "Ptychodiscus brevis") is a marinedinoflagellate common in Gulf of Mexico waters, and is the organism responsible for Floridared tide . "K. brevis" is a microscopic, single-celled, photosynthetic organism that can "bloom" (seealgal bloom ) frequently along Florida coastal waters. Each cell has twoflagella that allow it to move through the water in a spinning motion. "K. brevis" naturally produces a suite of potent neurotoxins collectively calledbrevetoxin s, which are responsible for large die-offs of marine organisms and seabirds.Red Tide is a condition when "Karenia brevis" has grown to very high concentrations and the water can take on a reddish or pinkish coloration. The region around southwest Florida is one of the major hotspots for red tide blooms. Red Tide outbreaks have been known to occur since the Spanish explorers of the 18th century.Algal species that have harmful effects either on the environment, or on Human Health are commonly known as Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs).
External links
* [http://www.floridamarine.org/features/view_article.asp?id=24936 Florida Marine Research Institute Page on Red Tides in Florida]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
