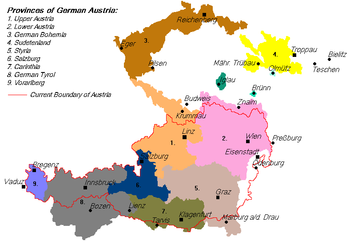
- German Bohemia
-
German Bohemia (German: Deutschböhmen; Czech: Německé Čechy) was a region in Czech Republic established, for a short period of time, after World War I. It included parts of northern and western Bohemia once largely populated by ethnic Germans. Important population centers were Liberec (Reichenberg), Ústí nad Labem (Aussig), Teplice (Teplitz-Schönau), Duchcov (Dux) , Cheb (Eger), Mariánské Lázně (Marienbad), Karlovy Vary (Karlsbad), Jablonec nad Nisou (Gablonz an der Neiße), Litoměřice (Leitmeritz), Most (Brüx) and Žatec (Saaz).
German Bohemians (Deutschböhmen, Čeští Němci) and German Moravians (Deutschmährer, Moravští Němci) also are alternative expressions for Sudeten Germans. Deutschböhmen and Deutschmährer are considered to be political neutral terms, while Sudeten Germans often is associated with German nationalistic tendencies within Sudeten German institutions.
Contents
History
Lands constituting German Bohemia were historically an integral part of the Habsburgs Kingdom of Bohemia but, with the imminent collapse of Habsburg Austria-Hungary at the end of World War I, areas of the Czech-majority Bohemia with an ethnic German majority who began to take actions to avoid joining a new Czechoslovak state. On 27 October 1918, the Egerland region declared independence from Bohemia and a day later the independence of Czechoslovakia was proclaimed in the Bohemian capital of Prague.
On 11 November 1918, Emperor Charles I of Austria relinquished power and, on 12 November, the ethnic German areas of the empire were declared the Republic of German Austria with the intent of unifying with Germany. The Province of German Bohemia (German: Provinz Deutschböhmen) was formed from the part of Bohemia containing the most ethnic Germans (however, ethnic German areas of southwestern Bohemia in the Bohemian Forest Region were added to Upper Austria instead of German Bohemia). The capital of the province was Liberec.
In late November 1918, the Czechoslovak army began an invasion of German Bohemia and during December it occupied whole area of the region with Liberec falling on 16 December and the last major city, Litoměřice, falling on 27 December 1918.
The status of German areas in Bohemia and Moravia was definitively settled by the 1919 peace treaties of Versailles and Saint-Germain-en-Laye that declared that the areas belong to Czechoslovakia. The Czechoslovak Government then granted amnesty for all activities against the new state.
The region was then reintegrated into the Bohemian Land of the First Republic of Czechoslovakia and remained a part of it until the Nazi dismemberment of Czechoslovakia when it was added to Sudetenland. This unlawful act was marked by a wholesale flight of the Czech minority that has already experienced the Nazi-sponsored militia - the Sudetendeutsche Freikorps (SFK) - violence and was afraid to stay with their erstwhile German neighbours. After World War II, the area was returned to Czechoslovakia. Most of the remaining German population living in the region following the War were expelled out of the country; many of these persons were killed or died during their flight from the attacking Czech and Soviet armies.
See also
Notes and references
External links
Categories:- Bohemia
- History of Austria
- Czech history
- German Austria
- 1918 disestablishments
- States and territories established in 1918
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.