- Utik
-
Ուտիք Province of Kingdom of Armenia, Caucasian Albania 189 BC–387 AD Capital Partav Historical era Antiquity, Middle Ages - Artaxias I declaring himself independent 189 BC - Seized by Albanians 387 AD Utik (Armenian: Ուտիք, also known as Uti, Utiq, or Outi, or Otena in Latin sources) was a historic province of the Kingdom of Armenia and a region of Caucasian Albania. Most of the region is located within present-day Azerbaijan immediately west of the Kura River while a part of it lies within the Tavush province of present-day northeastern Armenia.
Contents
History
According to Anania Shirakatsi's Ashkharatsuyts ("Geography" 7th c. AD), Utik was the 12th among the 15 provinces of the Kingdom of Armenia, and belonged, at the time, to the Kingdom of Aghvank (when the Utik and Artsakh provinces were disassociated from Armenia after its partition in the 4th century).[1] Utik was populated by the people called Utis, after whom it received its name. It is documented that after the Armenian reconquest in the 2nd century BC Utik also had Armenian population.[2][3][4][5][6]
Modern historians agree that "Utis" were a people of non-Armenian origin, and the modern ethnic group of Udi is their descendants.[7][8][9]
According to the Armenian geographer Anania Shirakatsi's Ashkharatsuyts, Utik consisted of 8 cantons (gavars, in Armenian): Aranrot, Tri, Rotparsyan, Aghve, Tuskstak (Tavush), Gardman, Shakashen, and Uti. The province was bounded by the Kura River from north-east, river Arax from south-east, and by the province of Artsakh from the west.[10]
Greco-Roman historians of 2nd century BC - 2nd century AD state that Utik was a province of Armenia, with the Kura River separating Armenia and Albania.[11][12][13] But the Armenian-Albanian boundary along the river Kura, confirmed by Greco-Roman sources, was often overrun by armies of both countries.[14]
According to Strabo, Armenia, which in the 6th c. BC had covered a large portion of Asia,[15] had lost some of its lands by the 2nd c. BC.[16] At the same time Strabo wrote: "According to report, Armenia, though a small country in earlier times, was enlarged by Artaxias and Zariadris". Around 190 BC, under the king Artashes I, Armenia re-conquered Vaspurakan and Paytakaran from Media, Acilisene from Cataonia, and Taron from Syria. Some have suggested that Utik was among the provinces re-conquered by Artashes I at this time,[6] though Strabo doesn't list Utik among Artashes' conquests.[16]
After the area between the Kura and Arax rivers (including Utik) passed to Albania in 387 AD, medieval Armenian historians (5th-7th centuries) referred to it as the "Plain of Aghvank." According to their chronicles, in the 2nd century BC Armenian king Vagharshak established the principality of Aghvank as part of the Kingdom of Armenia[citation needed], subjugating the "savage tribes" south of the Caucasus mountains, and appointing as its governor an Armenian nobleman by the name of Aran, who descended from the Armenian patriarch Hayk and was from the Armenian princely family of Sisakan. According to this account, members of the Sisakan family inherited Utik as well as the rest of the plain between the Arax and Kura rivers, which was later named "Plain of Aghvank" by the Sisakan princes (the entire area under Aran's governorship was named Aghuank (Albania, Greek) after the Sisakan nobles, who had fine (in Armenian--aghu) values).[3][4]
In 370s, after the King Urnayr of Aghvank had invaded Utik, Armenian sparapet Mushegh Mamikonyan defeated the Albanians, restoring the frontier back to the river Kura.[17] In 387 AD the Sassanid Empire helped the Albanians to seize from the Kingdom of Armenia a number of provinces, including Utik.[14] Subsequently, medieval Armenian historians often referred to the area as the "Plain of Aghvank."
In the middle of the 5th century by the order of the Persian king Peroz I the king Vache of Aghvank built in Utik the city initially called Perozapat, and later Partaw and Barda, and made it the capital of Aghvank.[18]
Starting with the 13th century, the area covered by Utik and Artsakh was called Karabakh by non-Armenians.[citation needed]
Population
In ancient times the area was inhabited by Armenians and "Utis," apparently after whom it was named.[19][20] Early Armenian chronicles (5th c. AD) state that the local princes of Utik descended from the Armenian noble family of Sisakan and spoke Armenian.[21] The origin of "Utis," whether an Armenian or non-Armenian tribe, remains obscure [9]
Utik had been one of the provinces of Greater Armenia, the population of which is referred to by the name Udini (or Utidorsi) in Latin sources, and by the name Outioi in Greek sources.[5] However, Ancient Greco-Roman writers placed Udis beyond Utik, north of the Kura River.[6]
Pliny the Elder calls "Utis" a Scythian tribe and also mentions so called utidors (which was apparently a tribe of mixed origin). Due to this a drift of ethnonym or more complex ethnogenetic processes are possible(for example, settlement of some Iranian-speaking or, less probably, Finno-Ugric peoples and adoption by them of language of the local Caucasian population).[6]
See also
References
- ^ Anania Shirakatsi. Geography
- ^ Chahin, Mark. The Kingdom of Armenia: A History. London: RoutledgeCurzon, 2001, p. 181 ISBN 0-7007-1452-9.
- ^ a b Movses Khorenatsi, "History of Armenia," I.13, II.8
- ^ a b Movses Kaghankatvatsi, "History of Aghvank," I.4
- ^ a b Wolfgang Schulze. The Language of the ‘Caucasian Albanian’ (Aluan) Palimpses
- ^ a b c d Igor Kuznetsov. Udis.
- ^ Robert H. Hewsen. "Ethno-History and the Armenian Influence upon the Caucasian Albanians," in: Samuelian, Thomas J. (Hg.), Classical Armenian Culture. Influences and Creativity, Chicago: 1982, 27-40.
- ^ (Russian) Shnirelman, Viktor A. Memory Wars: Myths, Identity and Politics in Transcaucasia. Moscow: Academkniga, 2003 ISBN 5-9462-8118-6, pp. 226-228.
- ^ a b Hewsen, Robert H. “The Kingdom of Artsakh,” in T. Samuelian & M. Stone, eds. Medieval Armenian Culture. Chico, CA, 1983
- ^ Anania Shirakatsi, "Geography"
- ^ Strabo, Geography, 11.14.4, http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/cgi-bin/ptext?doc=Perseus:text:1999.01.0198&loc=11.14.1
- ^ Pliny the Elder, "The Natural history ", 6.39: "..the tribe of Albanians settled on the Caucasian mountains, reaches ... the river Kir making border of Armenia and Iberia"
- ^ Claudius Ptolemy, "Geography" 5.12: "Armenia is located from the north to a part of Colchida, Iberia and Albania along the line, which goes through the river Kir (Kura)"
- ^ a b Encyclopedia Iranica. M. L. Chaumont. Albania.
- ^ Strabo, Geography, 11.13.5: "In ancient times Greater Armenia ruled the whole of Asia, after it broke up the empire of the Syrians", http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/cgi-bin/ptext?doc=Perseus:text:1999.01.0198&loc=11.13.1
- ^ a b Strabo, Geography, 11.14.5, http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/cgi-bin/ptext?doc=Perseus:text:1999.01.0198&loc=11.14.1
- ^ Pavstos Buzand, "History of Armenia," 5.13, 4th. c. AD.
- ^ Movses Kalankatuatsi. History of Albania
- ^ Armenian Soviet Encyclopedia, v. 6, p. 135, Yerevan 1980
- ^ Agathangelos, History of St. Gregory
- ^ Movses Khorenatsi, "History of Armenia," II.13, II.8
Regions of Kingdom of Armenia Traditional provinces or Ashkhars 1. Upper Armenia · 2. Sophene · 3. Aghdznik · 4. Turuberan · 5. Moxoene · 6. Corduene · 7. Parskahayk · 8. Vaspurakan · 9. Syunik · 10. Artsakh · 11. Paytakaran · 12. Utik · 13. Gugark · 14. Tayk · 15. Ayrarat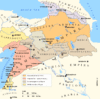
Other Armenian regions Provinces during the reign of Tigranes the Great Armenian Mesopotamia · Atropatene · Adiabene · Assyria · Iberia · Albania · Cappadocia · Cilicia · Judea · Osroene · Parthia · SyriaCategories:- Regions of old Armenia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.