- Cryptographic nonce
-
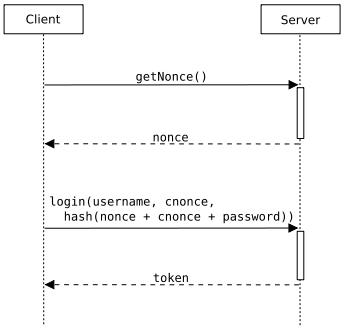 Typical client-server communication during a nonce-based authentication process including both a server nonce and a client nonce.
Typical client-server communication during a nonce-based authentication process including both a server nonce and a client nonce.
In security engineering, nonce is an arbitrary number used only once to sign a cryptographic communication. It is similar in spirit to a nonce word, hence the name. It is often a random or pseudo-random number issued in an authentication protocol to ensure that old communications cannot be reused in replay attacks. For instance, nonces are used in HTTP digest access authentication to calculate an MD5 digest of the password. The nonces are different each time the 401 authentication challenge response code is presented, thus making replay attacks virtually impossible. It is basically a cryptographic cookie.
A nonce may be used to ensure security for a stream cipher. Where the same key is used for more than one message then a different nonce is used to ensure that the keystream is different for different messages encrypted with that key. Often the message number is used.
Some also refer to initialization vectors as nonces for the above reasons. To ensure that a nonce is used only once, it should be time-variant (including a suitably fine-grained timestamp in its value), or generated with enough random bits to ensure a probabilistically insignificant chance of repeating a previously generated value. Some authors define pseudorandomness (or unpredictability) as a requirement for a nonce.[1]
See also
References
External links
- Sam Ruby Blogging on Nonce with an implementation
- RFC 2617 - HTTP Authentication: Basic and Digest Access Authentication
- RFC 3540 - Robust Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) Signaling with Nonces
- RFC 4418 - UMAC: Message Authentication Code using Universal Hashing
Categories:- Cryptography
- Cryptography stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
