- Dipole graph
-
Dipole graph 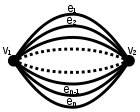
Vertices 2 Edges n Diameter 1 Chromatic number 2 Chromatic index n v · graph theory, a dipole graph (or dipole) is a multigraph consisting of two vertices connected with a number of edges. A dipole graph containing n edges is called the order-n dipole graph, and is denoted by Dn. The order-n dipole graph is dual to the cycle graph Cn. References
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Dipole Graph" from MathWorld.
- Jonathan L. Gross and Jay Yellen, 2006. Graph Theory and Its Applications, 2nd Ed., p. 17. Chapman & Hall/CRC. ISBN 1-58488-505-X

This combinatorics-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.v · Categories: - Combinatorics stubs
- Extensions and generalizations of graphs
- Parametric families of graphs
- Regular graphs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Dipole (disambiguation) — In physics, a dipole is a quantity involved some form of polarity Electric dipole Magnetic dipole Dipole moment (disambiguation) In meteorology: Arctic dipole anomaly Indian Ocean Dipole It may also refer to: Dipole antenna, a type of radio… … Wikipedia
Line graph — This article is about the mathematical concept. For statistical presentation method, see line chart. In graph theory, the line graph L(G) of undirected graph G is another graph L(G) that represents the adjacencies between edges of G. The name… … Wikipedia
List of graph theory topics — This is a list of graph theory topics, by Wikipedia page. See glossary of graph theory for basic terminology Contents 1 Examples and types of graphs 2 Graph coloring 3 Paths and cycles 4 … Wikipedia
List of mathematics articles (D) — NOTOC D D distribution D module D D Agostino s K squared test D Alembert Euler condition D Alembert operator D Alembert s formula D Alembert s paradox D Alembert s principle Dagger category Dagger compact category Dagger symmetric monoidal… … Wikipedia
Antenna (radio) — Whip antenna on car … Wikipedia
analysis — /euh nal euh sis/, n., pl. analyses / seez /. 1. the separating of any material or abstract entity into its constituent elements (opposed to synthesis). 2. this process as a method of studying the nature of something or of determining its… … Universalium
chemical bonding — ▪ chemistry Introduction any of the interactions that account for the association of atoms into molecules, ions, crystals, and other stable species that make up the familiar substances of the everyday world. When atoms approach one another … Universalium
cosmos — /koz meuhs, mohs/, n., pl. cosmos, cosmoses for 2, 4. 1. the world or universe regarded as an orderly, harmonious system. 2. a complete, orderly, harmonious system. 3. order; harmony. 4. any composite plant of the genus Cosmos, of tropical… … Universalium
radioactivity — /ray dee oh ak tiv i tee/, n. Physics, Chem. the phenomenon, exhibited by and being a property of certain elements, of spontaneously emitting radiation resulting from changes in the nuclei of atoms of the element. Also called activity. [1895… … Universalium
crystal — crystallike, adj. /kris tl/, n., adj., v., crystaled, crystaling or (esp. Brit.) crystalled, crystalling. n. 1. a clear, transparent mineral or glass resembling ice. 2. the transparent form of crystallized quartz. 3. Chem., Mineral. a solid body… … Universalium
18+© Academic, 2000-2025- Contact us: Technical Support, Advertising
Dictionaries export, created on PHP, Joomla, Drupal, WordPress, MODx.Share the article and excerpts
